5. Main Interface Window¶
The Main Interface Window is composed of several tabs and subtabs. The functions are described in detail in the following paragraphs, using these conventions:
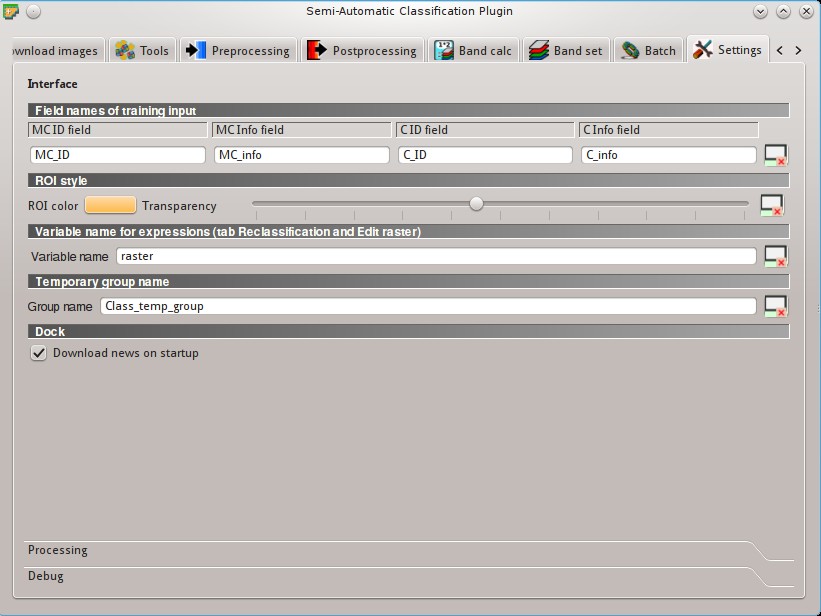
 = Configuration stored in the active project of QGIS
= Configuration stored in the active project of QGIS
 = Configuration stored in QGIS registry
= Configuration stored in QGIS registry
5.1. Download images¶
The tab  Download images includes the tools for searching and downloading free remote sensing images.
An internet connection is required.
Download images includes the tools for searching and downloading free remote sensing images.
An internet connection is required.
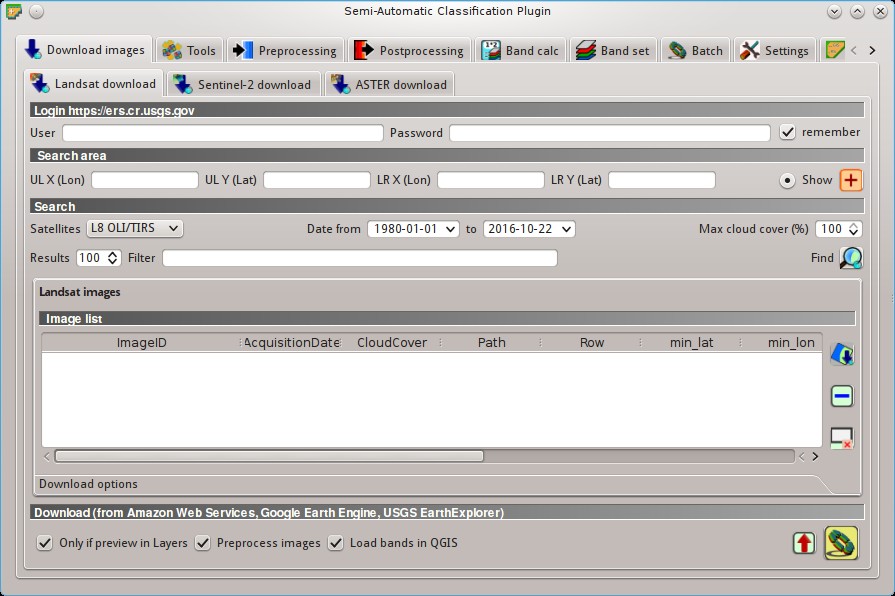
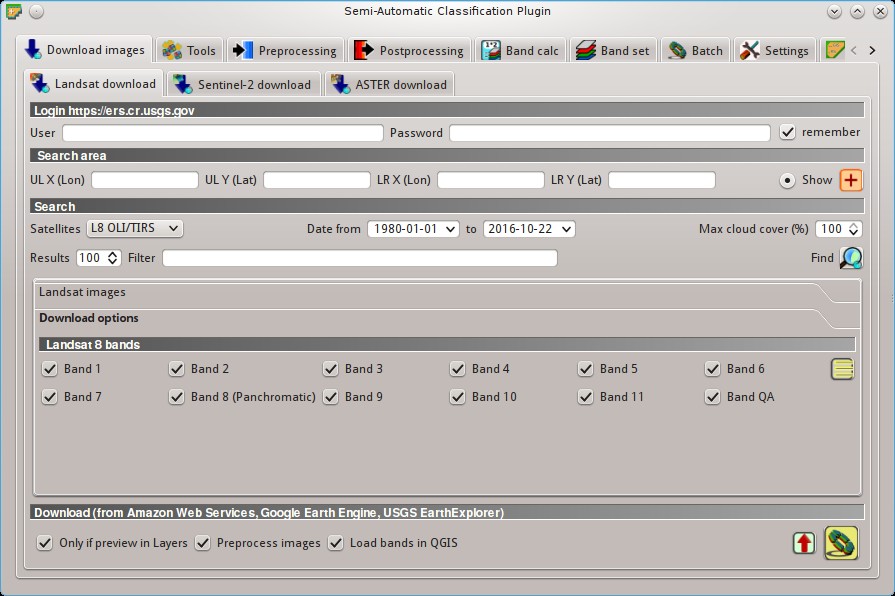
5.1.1. Landsat download¶
This tab allows for searching and downloading the whole archive of Landsat Satellite images (from 1 MSS to 8 OLI), acquired from the 80s to present days. Search is performed through the CMR Search API developed by NASA.
Landsat images are freely available through the services: EarthExplorer , Google Earth Engine , and the Amazon Web Services (AWS) (for Landsat 8). This tool attempts to download images first from Amazon Web Services and Google Earth Engine ; only if images are not available, the download is performed through the service EarthExplorer in order to prevent the server from becoming saturated.
Images are downloaded as compressed archives (this tool allows for the download of single bands for Landsat 8 images provided by the Amazon Web Services). Also, automatic conversion to reflectance of downloaded bands is available.
5.1.1.1. Login https://ers.cr.usgs.gov/¶
USGS EROS credentials (https://ers.cr.usgs.gov) are required for downloads from EarthExplorer . Login using your USGS EROS credentials or register for free at https://ers.cr.usgs.gov/register .
5.1.1.2. Search area¶
Define the search area by entering the coordinates (longitude and latitude) of an Upper Left (UL) point and Lower Right (LR) point, or interactively drawing an area in the map.
The definition of a search area is required before searching the images.
- UL X (Lon)
 : set the UL longitude;
: set the UL longitude; - UL Y (Lat)
 : set the UL latitude;
: set the UL latitude; - LR X (Lon)
 : set the LR longitude;
: set the LR longitude; - LR Y (Lat)
 : set the LR latitude;
: set the LR latitude;  Show: show or hide the search area drawn in the map;
Show: show or hide the search area drawn in the map; : define a search area by drawing a rectangle in the map; left click to set the UL point and right click to set the LR point; the area is displayed in the map;
: define a search area by drawing a rectangle in the map; left click to set the UL point and right click to set the LR point; the area is displayed in the map;
5.1.1.3. Search¶
Define the search settings such as date of acquisition, maximum cloud cover, or specify Landsat satellites.
Filter
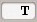 : set a filter such as the Image ID of Landsat images (e.g.
: set a filter such as the Image ID of Landsat images (e.g. LC81910312015006LGN00); it is possible to enter multiple Image IDs separated by comma or semicolon (e.g.LC81910312015006LGN00, LC81910312013224LGN00); filtered images must be inside the search area;Find
 : find the images in the search area; results are displayed inside the table in Landsat images; results are added to previous results;
: find the images in the search area; results are displayed inside the table in Landsat images; results are added to previous results;Tip: Search results (and the number thereof) depend on the defined area extent and the range of dates. In order to get more results, perform multiple searches defining smaller area extent and narrow acquisition dates (from and to).
5.1.1.4. Landsat images¶
 Image list: found images are displayed in this table, which includes the following fields;
Image list: found images are displayed in this table, which includes the following fields;- ImageID: the Landsat Image ID;
- AcquisitionDate: date of acquisition of Landsat image;
- CloudCover: percentage of cloud cover in the image;
- Path: WRS path of the image;
- Row: WRS row of the image;
- min_lat: minimum latitude of the image;
- min_lon: minimum longitude of the image;
- max_lat: maximum latitude of the image;
- max_lon: maximum longitude of the image;
- USGScollection: USGS collection code of the image;
- Preview: URL of the image preview;
- collection: collection code of the image;
 : display preview of highlighted images in the map; preview is roughly georeferenced on the fly;
: display preview of highlighted images in the map; preview is roughly georeferenced on the fly; : remove highlighted images from the list;
: remove highlighted images from the list; : remove all images from the list;
: remove all images from the list;
5.1.1.5. Download options¶
Landsat 8 bands
This tab allows for the selection of single bands (only for Landsat 8 images provided by the Amazon Web Services).
5.1.1.6. Download¶
Download the Landsat images in the Landsat images. During the download it is recommended not to interact with QGIS.
Download is performed according to image availability from the services EarthExplorer , Google Earth Engine , or the Amazon Web Services (AWS) . If the image is not available for download it is possible to check the availability thereof on http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ .
 Only if preview in Layers: if checked, download only those images listed in Landsat images which are also listed in the QGIS layer panel;
Only if preview in Layers: if checked, download only those images listed in Landsat images which are also listed in the QGIS layer panel; Preprocess images: if checked, bands are automatically converted after the download, according to the settings defined in Landsat;
Preprocess images: if checked, bands are automatically converted after the download, according to the settings defined in Landsat; Load bands in QGIS: if checked, bands are loaded in QGIS after the download;
Load bands in QGIS: if checked, bands are loaded in QGIS after the download; : export the download links to a text file;
: export the download links to a text file; : start the download process of all the images listed in Landsat images;
: start the download process of all the images listed in Landsat images;
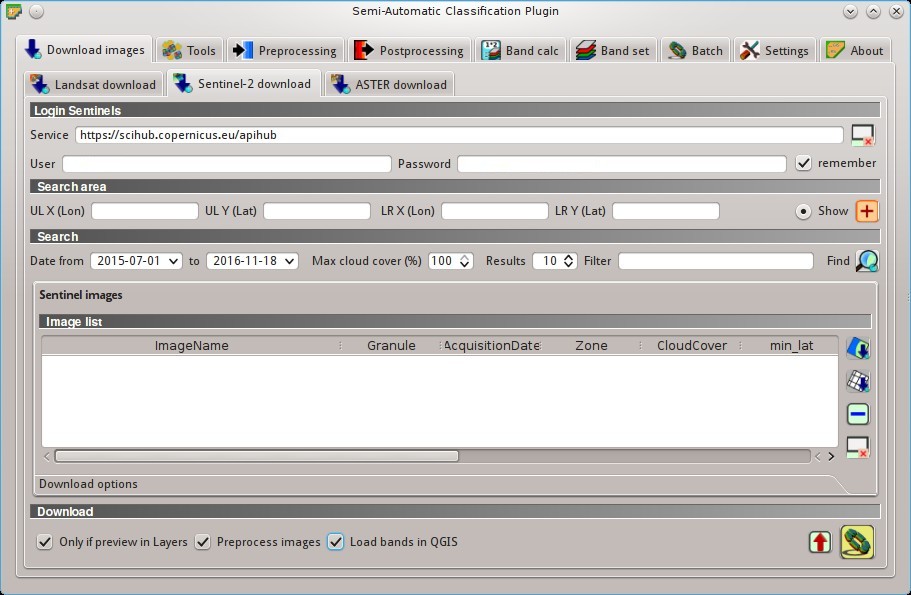
5.1.2. Sentinel-2 download¶
Sentinel-2 is a European satellite launched in 2015, developed in the frame of Copernicus land monitoring services, which acquires 13 spectral bands (see Sentinel-2 Satellite). This tab allows for searching and downloading the free Sentinel-2 images (Level-1C) from the Sentinels Scientific Data Hub (using the Data Hub API ). Images are mainly downloaded from the Amazon S3 AWS if available.
Sentinel-2 satellite has a swath width of 290km. Sentinel-2 Level-1C images are delivered in granules (also called tiles) with a side of 100km in UTM/WGS84 projection. This tool allows for the selection and download of granules and bands.
Tip: In case of errors please see Error [50] ‘Internet error’. Unable to download Sentinel-2 images. Why? and Error [56] ‘SSL connection error’. Unable to download Sentinel-2 images. Why?.
5.1.2.1. Login Sentinels¶
In order to access to Sentinel data a free registration is required at https://scihub.copernicus.eu/userguide/1SelfRegistration (other services may require different registrations). After the registration, enter the user name and password for accessing data.
- Service

 : enter the service URL (default is https://scihub.copernicus.eu/apihub); other mirror services that share the same infrastructure can be used (such as https://scihub.copernicus.eu/dhus , https://finhub.nsdc.fmi.fi , https://data.sentinel.zamg.ac.at);
: enter the service URL (default is https://scihub.copernicus.eu/apihub); other mirror services that share the same infrastructure can be used (such as https://scihub.copernicus.eu/dhus , https://finhub.nsdc.fmi.fi , https://data.sentinel.zamg.ac.at);  : reset the default service https://scihub.copernicus.eu/s2);
: reset the default service https://scihub.copernicus.eu/s2);- User

 : enter the user name;
: enter the user name; - Password

 : enter the password;
: enter the password;  remember: remember user name and password in QGIS;
remember: remember user name and password in QGIS;
5.1.2.2. Search area¶
Define the search area by entering the coordinates (longitude and latitude) of an Upper Left (UL) point and Lower Right (LR) point, or interactively drawing an area in the map.
The definition of a search area is required before searching the images.
- UL X (Lon)
 : set the UL longitude;
: set the UL longitude; - UL Y (Lat)
 : set the UL latitude;
: set the UL latitude; - LR X (Lon)
 : set the LR longitude;
: set the LR longitude; - LR Y (Lat)
 : set the LR latitude;
: set the LR latitude;  Show: show or hide the search area drawn in the map;
Show: show or hide the search area drawn in the map; : define a search area by drawing a rectangle in the map; left click to set the UL point and right click to set the LR point; the area is displayed in the map;
: define a search area by drawing a rectangle in the map; left click to set the UL point and right click to set the LR point; the area is displayed in the map;
5.1.2.3. Search¶
Define search settings such as the date of acquisition or search for specific Sentinel images using the Image ID or name.
Filter
 : set a filter such as the Image Name of Sentinel images (e.g.
: set a filter such as the Image Name of Sentinel images (e.g. S2A_OPER_PRD_MSIL1C_PDMC_20160419T190217_R022_V20160419T101026);Find
 : find the images in the search area; results are displayed inside the table in Sentinel images; results are added to previous results;
: find the images in the search area; results are displayed inside the table in Sentinel images; results are added to previous results;Tip: Search results (and the number thereof) depend on the defined area extent and the range of dates. In order to get more results, perform multiple searches defining smaller area extent and narrow acquisition dates (from and to).
5.1.2.4. Sentinel images¶
 Image list: found images are displayed in this table, which includes the following fields;
Image list: found images are displayed in this table, which includes the following fields;- ImageName: the Sentinel Image Name;
- Granule: the single granule name;
- AcquisitionDate: date of acquisition of Sentinel image;
- Zone: tile zone according to the US-MGRS naming convention;
- CloudCover: percentage of cloud cover in the image;
- min_lat: minimum latitude of the image;
- min_lon: minimum longitude of the image;
- max_lat: maximum latitude of the image;
- max_lon: maximum longitude of the image;
- Size: the size of the image (unused);
- Preview: URL of the image overview;
- GranulePreview: URL of the granule preview; if available, preview is downloaded from the Amazon Web Services ;
- ImageID: the Sentinel Image ID;
 : display overview of highlighted images in the map; overview is roughly georeferenced on the fly; overviews could not be available when using mirror services;
: display overview of highlighted images in the map; overview is roughly georeferenced on the fly; overviews could not be available when using mirror services; : remove all images from the list;
: remove all images from the list;Tip: download this zip file containing the shapefile of Sentinel-2 granules for identifying the zone; load this shapefile in QGIS, select the granules in your search area and open the attribute table to see the zone name.
5.1.2.5. Download options¶
This tab allows for the selection of single bands.
5.1.2.6. Download¶
Download the Sentinel-2 images in the Sentinel images. Bands selected in Download options are downloaded.
During the download it is recommended not to interact with QGIS.
 Only if preview in Layers: if checked, download only those images listed in Sentinel images which are also listed in the QGIS layer panel;
Only if preview in Layers: if checked, download only those images listed in Sentinel images which are also listed in the QGIS layer panel; Preprocess images: if checked, bands are automatically converted after the download, according to the settings defined in Sentinel-2;
Preprocess images: if checked, bands are automatically converted after the download, according to the settings defined in Sentinel-2; Load bands in QGIS: if checked, bands are loaded in QGIS after the download;
Load bands in QGIS: if checked, bands are loaded in QGIS after the download; : export the download links to a text file;
: export the download links to a text file; : start the download process of all the images listed in Sentinel images;
: start the download process of all the images listed in Sentinel images;
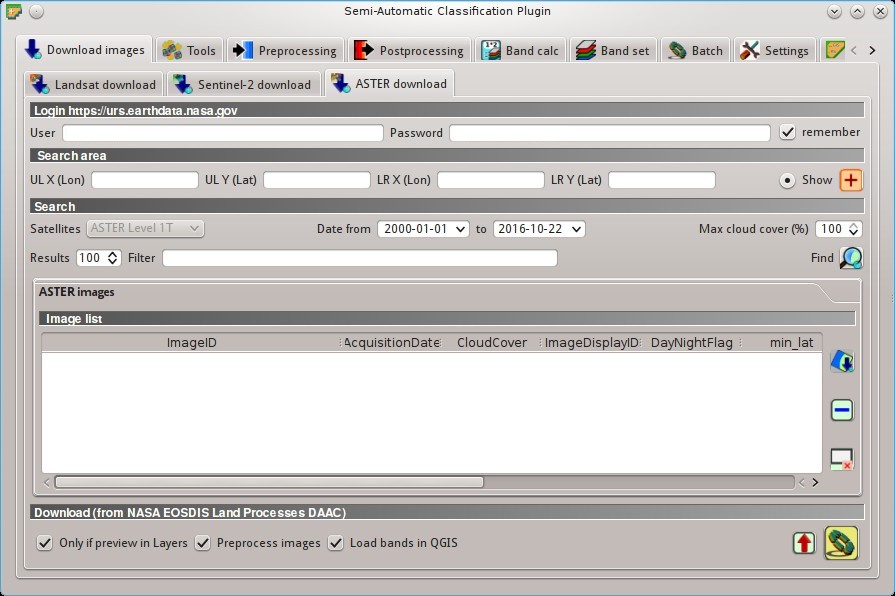
5.1.3. ASTER download¶
This tab allows for searching and downloading the whole archive of free images L1T acquired by ASTER Satellite since 2000. Search is performed through the CMR Search API developed by NASA. The ASTER L1T data products are retrieved from the online Data Pool, courtesy of the NASA Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (LP DAAC), USGS/Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/data_access/data_pool.
Also, automatic conversion to reflectance of downloaded bands is available.
5.1.3.1. Login https://urs.earthdata.nasa.gov¶
EOSDIS Earthdata credentials (https://urs.earthdata.nasa.gov ) are required for download. Login using your EOSDIS Earthdata credentials or register for free at https://urs.earthdata.nasa.gov/users/new .
Warning: Before downloading ASTER images, you must approve LP DAAC Data Pool clicking the following https://urs.earthdata.nasa.gov/approve_app?client_id=ijpRZvb9qeKCK5ctsn75Tg
5.1.3.2. Search area¶
Define the search area by entering the coordinates (longitude and latitude) of an Upper Left (UL) point and Lower Right (LR) point, or interactively drawing an area in the map.
The definition of a search area is required before searching the images.
- UL X (Lon)
 : set the UL longitude;
: set the UL longitude; - UL Y (Lat)
 : set the UL latitude;
: set the UL latitude; - LR X (Lon)
 : set the LR longitude;
: set the LR longitude; - LR Y (Lat)
 : set the LR latitude;
: set the LR latitude;  Show: show or hide the search area drawn in the map;
Show: show or hide the search area drawn in the map; : define a search area by drawing a rectangle in the map; left click to set the UL point and right click to set the LR point; the area is displayed in the map;
: define a search area by drawing a rectangle in the map; left click to set the UL point and right click to set the LR point; the area is displayed in the map;
5.1.3.3. Search¶
Define the search settings such as date of acquisition, maximum cloud cover, or specify ASTER satellites.
Filter
 : set a filter such as the Image ID of ASTER images; it is possible to enter multiple Image IDs separated by comma or semicolon; filtered images must be inside the search area;
: set a filter such as the Image ID of ASTER images; it is possible to enter multiple Image IDs separated by comma or semicolon; filtered images must be inside the search area;Find
 : find the images in the search area; results are displayed inside the table in ASTER images; results are added to previous results;
: find the images in the search area; results are displayed inside the table in ASTER images; results are added to previous results;Tip: Search results (and the number thereof) depend on the defined area extent and the range of dates. In order to get more results, perform multiple searches defining smaller area extent and narrow acquisition dates (from and to).
5.1.3.4. ASTER images¶
 Image list: found images are displayed in this table, which includes the following fields;
Image list: found images are displayed in this table, which includes the following fields;- ImageID: the ASTER Image ID;
- AcquisitionDate: date of acquisition of ASTER image;
- CloudCover: percentage of cloud cover in the image;
- ImageDisaplyID: the ASTER Image ID;
- DayNightFlag: flag for acquisition during day or night;
- min_lat: minimum latitude of the image;
- min_lon: minimum longitude of the image;
- max_lat: maximum latitude of the image;
- max_lon: maximum longitude of the image;
- Service: download service of the image;
- Preview: URL of the image preview;
- collection: collection code of the image;
 : display preview of highlighted images in the map; preview is roughly georeferenced on the fly;
: display preview of highlighted images in the map; preview is roughly georeferenced on the fly; : remove highlighted images from the list;
: remove highlighted images from the list; : remove all images from the list;
: remove all images from the list;
5.1.3.5. Download¶
Download the ASTER images in the ASTER images. During the download it is recommended not to interact with QGIS.
 Only if preview in Layers: if checked, download only those images listed in ASTER images which are also listed in the QGIS layer panel;
Only if preview in Layers: if checked, download only those images listed in ASTER images which are also listed in the QGIS layer panel; Preprocess images: if checked, bands are automatically converted after the download, according to the settings defined in ASTER;
Preprocess images: if checked, bands are automatically converted after the download, according to the settings defined in ASTER; Load bands in QGIS: if checked, bands are loaded in QGIS after the download;
Load bands in QGIS: if checked, bands are loaded in QGIS after the download; : export the download links to a text file;
: export the download links to a text file; : start the download process of all the images listed in ASTER images;
: start the download process of all the images listed in ASTER images;
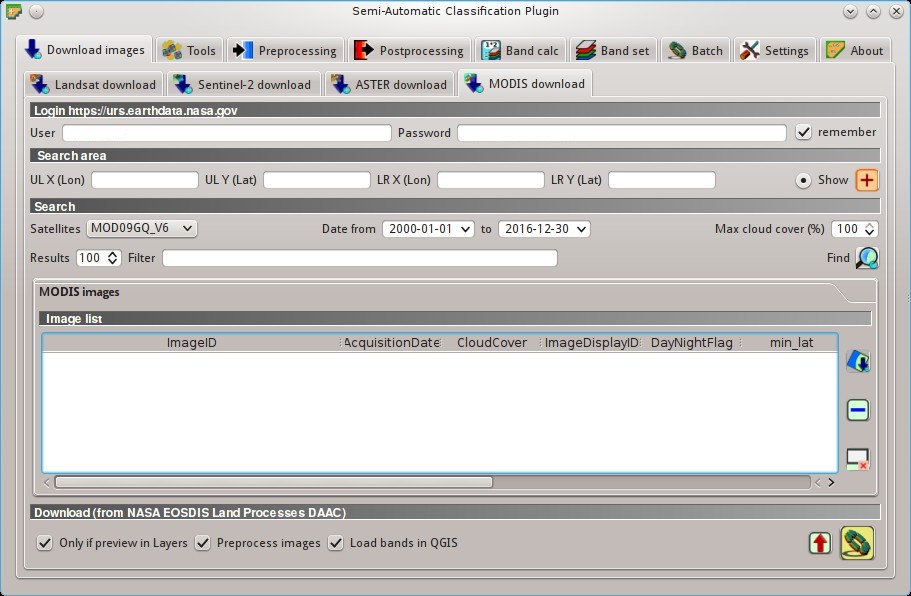
5.1.4. MODIS download¶
This tab allows for searching and downloading the archive of free MODIS Products acquired since 2000 (in particular MOD09GQ, MYD09GQ, MOD09GA, MYD09GA, MOD09Q1, MYD09Q1, MOD09A1, MYD09A1). Search is performed through the CMR Search API developed by NASA. MODIS products are retrieved from the online Data Pool, courtesy of the NASA Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (LP DAAC), USGS/Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/data_access/data_pool.
Also, automatic reprojection of downloaded bands is available.
5.1.4.1. Login https://urs.earthdata.nasa.gov¶
EOSDIS Earthdata credentials (https://urs.earthdata.nasa.gov ) are required for download. Login using your EOSDIS Earthdata credentials or register for free at https://urs.earthdata.nasa.gov/users/new .
Warning: Before downloading MODIS images, you must approve LP DAAC Data Pool clicking the following https://urs.earthdata.nasa.gov/approve_app?client_id=ijpRZvb9qeKCK5ctsn75Tg
5.1.4.2. Search area¶
Define the search area by entering the coordinates (longitude and latitude) of an Upper Left (UL) point and Lower Right (LR) point, or interactively drawing an area in the map.
The definition of a search area is required before searching the images.
- UL X (Lon)
 : set the UL longitude;
: set the UL longitude; - UL Y (Lat)
 : set the UL latitude;
: set the UL latitude; - LR X (Lon)
 : set the LR longitude;
: set the LR longitude; - LR Y (Lat)
 : set the LR latitude;
: set the LR latitude;  Show: show or hide the search area drawn in the map;
Show: show or hide the search area drawn in the map; : define a search area by drawing a rectangle in the map; left click to set the UL point and right click to set the LR point; the area is displayed in the map;
: define a search area by drawing a rectangle in the map; left click to set the UL point and right click to set the LR point; the area is displayed in the map;
5.1.4.3. Search¶
Define the search settings such as date of acquisition, maximum cloud cover, or specify MODIS product.
Max cloud cover (%)
 : maximum cloud cover in the image (unused);
: maximum cloud cover in the image (unused);Filter
 : set a filter such as the Image ID of MODIS images; it is possible to enter multiple Image IDs separated by comma or semicolon; filtered images must be inside the search area;
: set a filter such as the Image ID of MODIS images; it is possible to enter multiple Image IDs separated by comma or semicolon; filtered images must be inside the search area;Find
 : find the images in the search area; results are displayed inside the table in MODIS images; results are added to previous results;
: find the images in the search area; results are displayed inside the table in MODIS images; results are added to previous results;Tip: Search results (and the number thereof) depend on the defined area extent and the range of dates. In order to get more results, perform multiple searches defining smaller area extent and narrow acquisition dates (from and to).
5.1.4.4. MODIS images¶
 Image list: found images are displayed in this table, which includes the following fields;
Image list: found images are displayed in this table, which includes the following fields;- ImageID: the MODIS Image ID;
- AcquisitionDate: date of acquisition of MODIS image;
- CloudCover: percentage of cloud cover in the image;
- ImageDisaplyID: the MODIS Image ID;
- DayNightFlag: flag for acquisition during day or night;
- min_lat: minimum latitude of the image;
- min_lon: minimum longitude of the image;
- max_lat: maximum latitude of the image;
- max_lon: maximum longitude of the image;
- Service: download service of the image;
- Preview: URL of the image preview;
- collection: collection code of the image;
 : display preview of highlighted images in the map; preview is roughly georeferenced on the fly;
: display preview of highlighted images in the map; preview is roughly georeferenced on the fly; : remove highlighted images from the list;
: remove highlighted images from the list; : remove all images from the list;
: remove all images from the list;
5.1.4.5. Download¶
Download the MODIS images in the MODIS images. During the download it is recommended not to interact with QGIS.
 Only if preview in Layers: if checked, download only those images listed in MODIS images which are also listed in the QGIS layer panel;
Only if preview in Layers: if checked, download only those images listed in MODIS images which are also listed in the QGIS layer panel; Preprocess images: if checked, bands are automatically converted after the download, according to the settings defined in MODIS;
Preprocess images: if checked, bands are automatically converted after the download, according to the settings defined in MODIS; Load bands in QGIS: if checked, bands are loaded in QGIS after the download;
Load bands in QGIS: if checked, bands are loaded in QGIS after the download; : export the download links to a text file;
: export the download links to a text file; : start the download process of all the images listed in MODIS images;
: start the download process of all the images listed in MODIS images;
5.2. Tools¶
The tab 
Tools includes several tools for manipulating ROIs and spectral signatures.
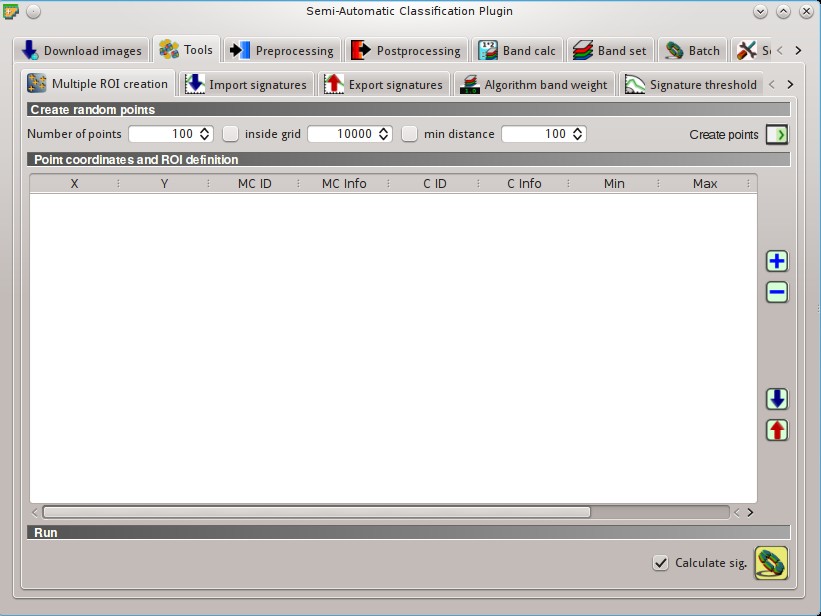
5.2.1. Multiple ROI Creation¶
This tab allows for the automatic creation of ROIs, useful for the rapid classification of multi-temporal images, or for accuracy assessment. Given a list of point coordinates and ROI options, this tool performs the region growing of ROIs. Created ROIs are automatically saved to the Training input.
5.2.1.1. Create random points¶
- Number of points
 : set a number of points that will be created when Create points
: set a number of points that will be created when Create points  is clicked;
is clicked;  inside grid
inside grid  : if checked, the input image area is divided in cells where the size thereof is defined in the combobox (image unit, usually meters); points defined in
: if checked, the input image area is divided in cells where the size thereof is defined in the combobox (image unit, usually meters); points defined in Number of random pointsare created randomly within each cell; min distance
min distance  : if checked, random points have a minimum distance defined in the combobox (image unit, usually meters); setting a minimum distance can result in fewer points than the number defined in Number of points;
: if checked, random points have a minimum distance defined in the combobox (image unit, usually meters); setting a minimum distance can result in fewer points than the number defined in Number of points;- Create points
 : create random points inside the input image area;
: create random points inside the input image area;
5.2.1.2. Point coordinates and ROI definition¶
 Point coordinates and ROI definition: table containing the following fields;
Point coordinates and ROI definition: table containing the following fields;- X : point X coordinate (float);
- Y : point Y coordinate (float);
- MC ID: ROI Macroclass ID (int);
- MC Info: ROI Macroclass information (text);
- C ID: ROI Class ID (int);
- C Info: ROI Class information (text);
- Min : the minimum area of a ROI (in pixel unit);
- Max : the maximum width of a ROI (in pixel unit);
- Dist : the interval which defines the maximum spectral distance between the seed pixel and the surrounding pixels (in radiometry unit);
- Rapid ROI band : if a band number is defined, ROI is created only using the selected band, similarly to Rapid ROI band in ROI creation ;
 : add a new row to the table; all the table fields must be filled for the ROI creation;
: add a new row to the table; all the table fields must be filled for the ROI creation; : delete the highlighted rows from the table;
: delete the highlighted rows from the table; : import a point list from text file to the table; every line of the text file must contain values separated by tabs of
: import a point list from text file to the table; every line of the text file must contain values separated by tabs of X,Y,MC ID,MC Info,Class ID,C Info,Min,Max,Dist, and optionally theRapid ROI band; : export the point list to text file;
: export the point list to text file;
5.2.1.3. Run¶
 Calculate sig.: if checked, the spectral signature is calculated while the ROI is saved to Training input;
Calculate sig.: if checked, the spectral signature is calculated while the ROI is saved to Training input; : start the ROI creation process for all the points and save ROIs to the Training input;
: start the ROI creation process for all the points and save ROIs to the Training input;
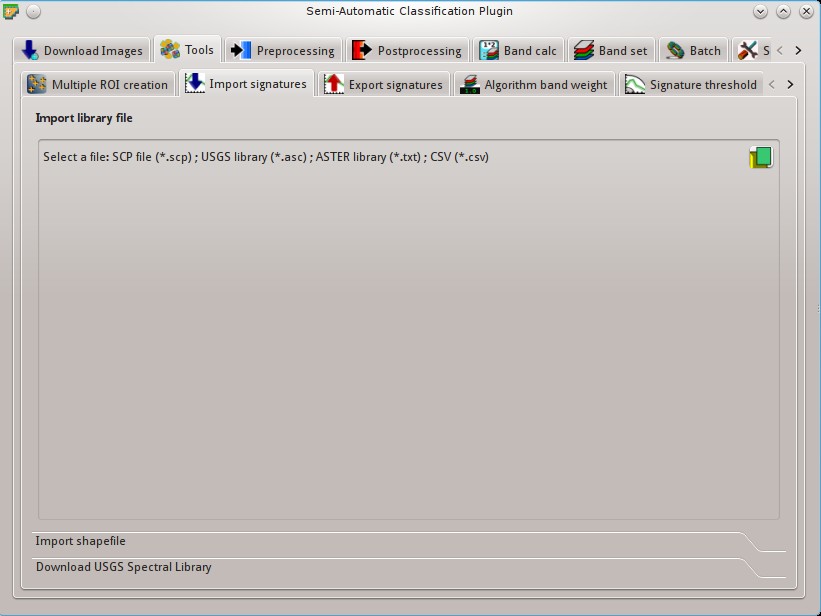
5.2.2. Import signatures¶
The tab  Import signatures allows for importing spectral signatures from various sources.
Import signatures allows for importing spectral signatures from various sources.
5.2.2.1. Import library file¶
This tool allows for importing spectral signatures from various sources: a previously saved Training input (.scp file); a USGS Spectral Library (.asc file); a previously exported CSV file. In case of USGS Spectral Library, the library is automatically sampled according to the image band wavelengths defined in the Band set, and added to the ROI Signature list;
- Select a file
 : open a file to be imported in the Training input;
: open a file to be imported in the Training input;
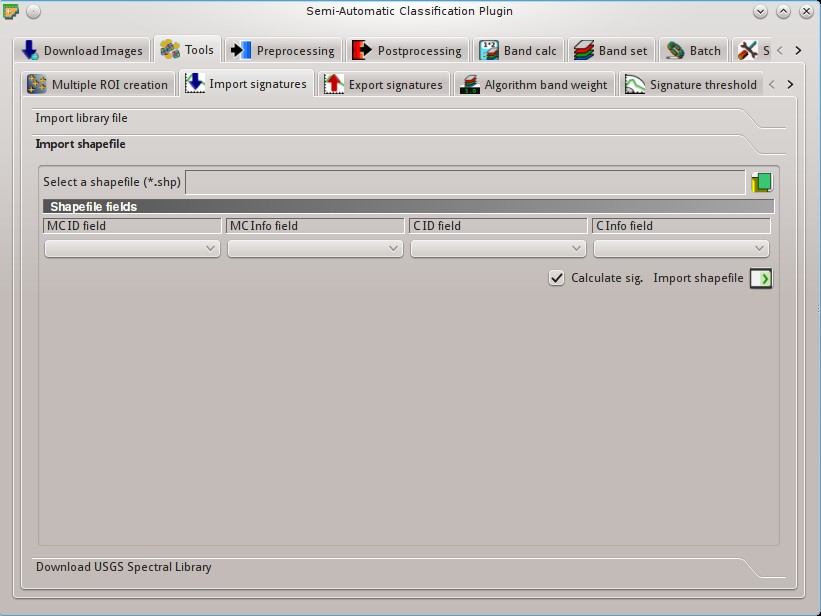
5.2.2.2. Import shapefile¶
This tool allows for importing a shapefile, selecting the corresponding fields of the Training input.
- Select a shapefile
 : open a shapefile;
: open a shapefile; - MC ID field
 : select the shapefile field corresponding to MC ID;
: select the shapefile field corresponding to MC ID; - MC Info field
 : select the shapefile field corresponding to MC Info;
: select the shapefile field corresponding to MC Info; - C ID field
 : select the shapefile field corresponding to C ID;
: select the shapefile field corresponding to C ID; - C Info field
 : select the shapefile field corresponding to C Info;
: select the shapefile field corresponding to C Info;  Calculate sig.: if checked, the spectral signature is calculated while the ROI is saved to Training input;
Calculate sig.: if checked, the spectral signature is calculated while the ROI is saved to Training input;- Import shapefile
 : import all the shapefile polygons as ROIs in the Training input;
: import all the shapefile polygons as ROIs in the Training input;
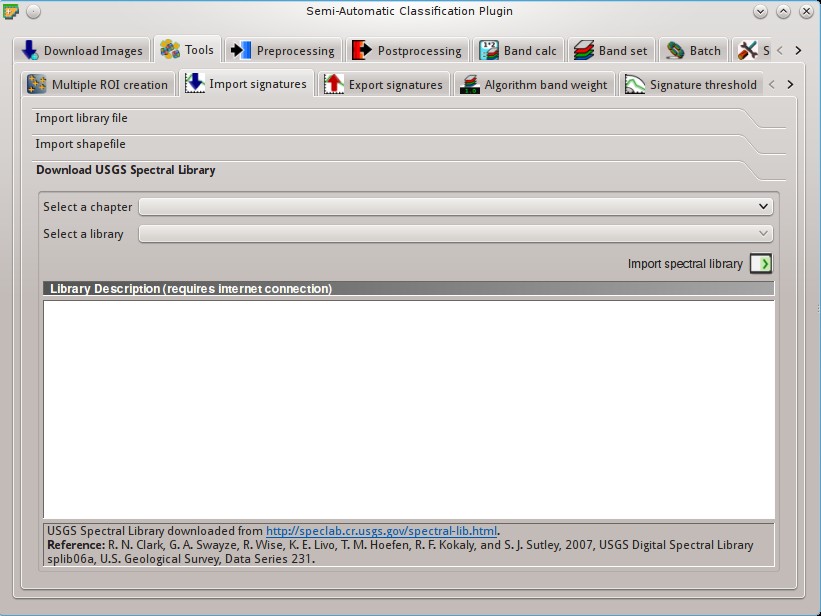
5.2.2.3. Download USGS Spectral Library¶
The tab Download USGS Spectral Library allows for the download of the USGS spectral library (Clark, R.N., Swayze, G.A., Wise, R., Livo, E., Hoefen, T., Kokaly, R., Sutley, S.J., 2007, USGS digital spectral library splib06a: U.S. Geological Survey, Digital Data Series 231).
The libraries are grouped in chapters including Minerals, Mixtures, Coatings, Volatiles, Man-Made, Plants, Vegetation Communities, Mixtures with Vegetation, and Microorganisms. An internet connection is required.
Select a chapter
 : select one of the library chapters; after the selection, chapter libraries are shown in Select a library;
: select one of the library chapters; after the selection, chapter libraries are shown in Select a library;Select a library
 : select one of the libraries; the library description is displayed in the frame Library description;
: select one of the libraries; the library description is displayed in the frame Library description;Import spectral library
 : download the library and add the sampled spectral signature to the ROI Signature list using the parameters defined in ROI creation; the library is automatically sampled according to the image band wavelengths defined in the Band set, and added to the ROI Signature list;
: download the library and add the sampled spectral signature to the ROI Signature list using the parameters defined in ROI creation; the library is automatically sampled according to the image band wavelengths defined in the Band set, and added to the ROI Signature list;Tip: Spectral libraries downloaded from the
USGS Spectral Librarycan be used with Minimum Distance or Spectral Angle Mapping algorithms, but not Maximum Likelihood because this algorithm needs the covariance matrix that is not included in the spectral libraries.
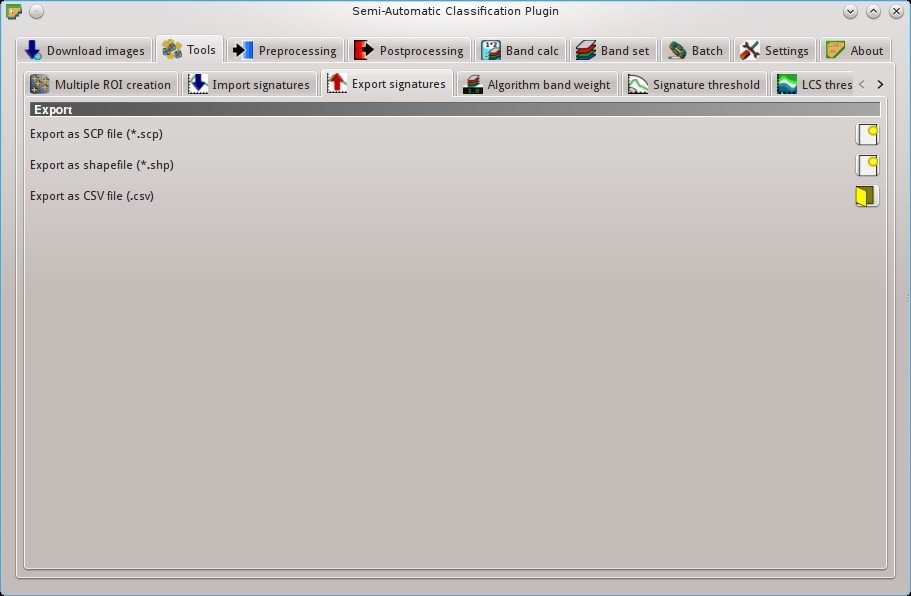
5.2.3. Export signatures¶
This tool allows for exporting the signatures highlighted in the ROI Signature list.
- Export as SCP file
 : create a new .scp file and export highlighted ROIs and spectral signatures as SCP file (* .scp);
: create a new .scp file and export highlighted ROIs and spectral signatures as SCP file (* .scp); - Export as shapefile
 : export highlighted ROIs (spectral signature data excluded) as a new shapefile (* .shp);
: export highlighted ROIs (spectral signature data excluded) as a new shapefile (* .shp); - Export as CSV file
 : open a directory, and export highlighted spectral signatures as individual CSV files (* .csv) separated by semicolon ( ; );
: open a directory, and export highlighted spectral signatures as individual CSV files (* .csv) separated by semicolon ( ; );
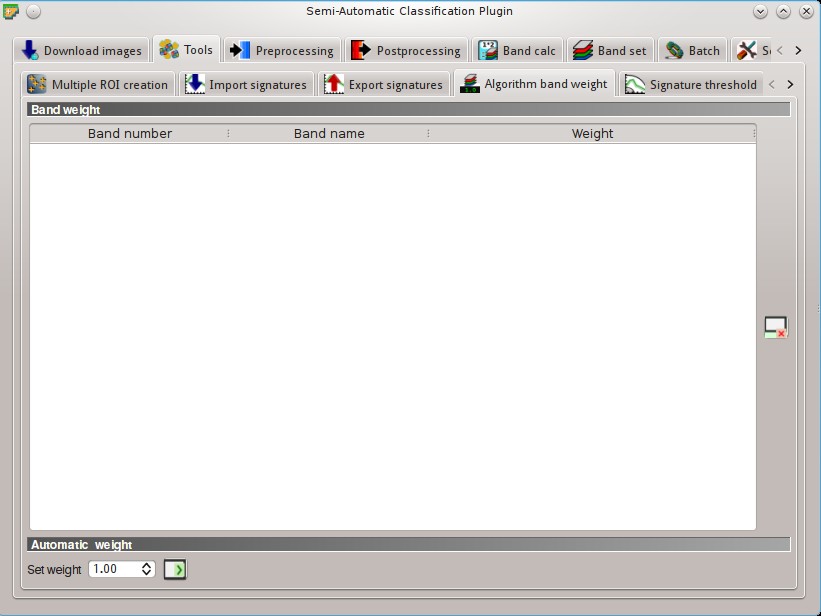
5.2.4. Algorithm band weight¶
This tab allows for the definition of band weights that are useful for improving the spectral separability of materials at certain wavelengths (bands). During the classification process, band values and spectral signature values are multiplied by the corresponding band weights, thus modifying the spectral distances.
5.2.4.1. Band weight¶
5.2.4.2. Automatic weight¶
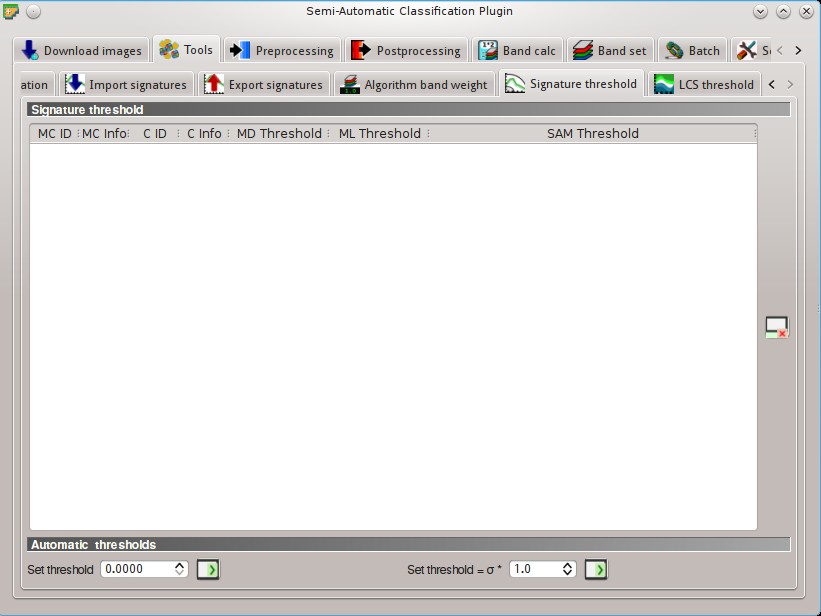
5.2.5. Signature threshold¶
This tab allows for the definition of a classification threshold for each spectral signature. All the signatures contained in the Training input are listed. This is useful for improving the classification results, especially when spectral signatures are similar. Thresholds of signatures are saved in the Training input.
If threshold is 0 then no threshold is applied. Depending on the selected Classification algorithm the threshold value is evaluated differently:
- for Minimum Distance, pixels are unclassified if distance is greater than threshold value;
- for Maximum Likelihood, pixels are unclassified if probability is less than threshold value (max 100);
- for Spectral Angle Mapping, pixels are unclassified if spectral angle distance is greater than threshold value (max 90).
5.2.5.1. Signature threshold¶
 Signature threshold: table containing the following fields;
Signature threshold: table containing the following fields;- MC ID: signature Macroclass ID;
- MC Info: signature Macroclass Information;
- C ID: signature Class ID;
- C Info: signature Class Information;
- MD Threshold: Minimum Distance threshold; this value can be edited;
- ML Threshold: Maximum Likelihood threshold; this value can be edited;
- SAM Threshold: Spectral Angle Mapping threshold; this value can be edited;
 : reset all signatures thresholds to 0 (i.e. no threshold used);
: reset all signatures thresholds to 0 (i.e. no threshold used);
5.2.5.2. Automatic thresholds¶
- Set threshold

 : set the defined value as threshold for all the highlighted signatures in the table;
: set the defined value as threshold for all the highlighted signatures in the table; - Set threshold = σ *

 : for all the highlighted signatures, set an automatic threshold calculated as the distance (or angle) between mean signature and (mean signature + (σ * v)), where σ is the standard deviation and v is the defined value; currently works for Minimum Distance and Spectral Angle Mapping;
: for all the highlighted signatures, set an automatic threshold calculated as the distance (or angle) between mean signature and (mean signature + (σ * v)), where σ is the standard deviation and v is the defined value; currently works for Minimum Distance and Spectral Angle Mapping;
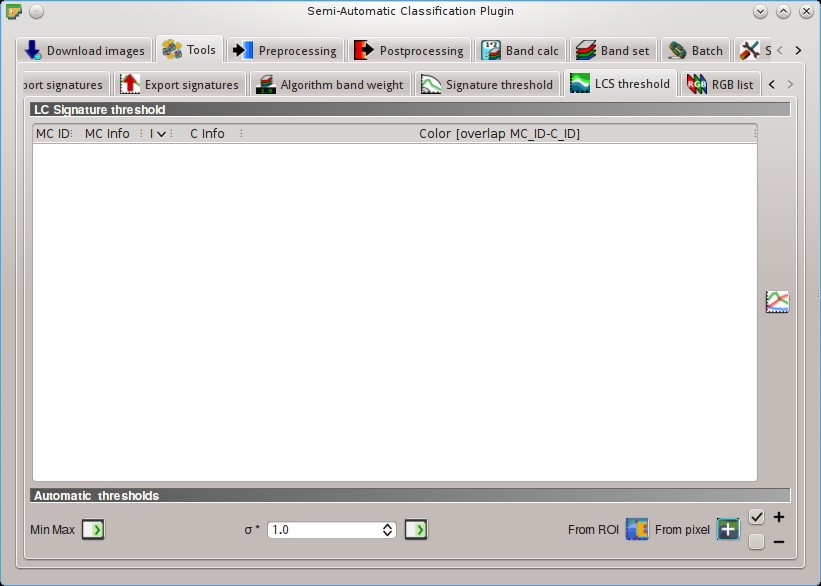
5.2.6. LCS threshold¶
This tab allows for setting the signature thresholds used by Land Cover Signature Classification. All the signatures contained in the Training input are listed; also, signature thresholds are saved in the Training input.
Overlapping signatures (belonging to different classes or macroclasses) are highlighted in orange in the table LC Signature threshold; the overlapping check is performed considering MC ID or C ID according to the setting Use  MC ID
MC ID  C ID in Classification algorithm.
Overlapping signatures sharing the same ID are not highlighted.
C ID in Classification algorithm.
Overlapping signatures sharing the same ID are not highlighted.
5.2.6.1. LC Signature threshold¶
 LC Signature threshold: table containing the following fields;
LC Signature threshold: table containing the following fields;- MC ID: signature Macroclass ID;
- MC Info: signature Macroclass Information;
- C ID: signature Class ID;
- C Info: signature Class Information;
- Color [overlap MC_ID-C_ID]: signature color; also, the combination MC ID-C ID is displayed in case of overlap with other signatures (see Land Cover Signature Classification);
- Min B
X: minimum value of bandX; this value can be edited; - Max B
X: maximum value of bandX; this value can be edited;
 : show the ROI spectral signature in the Spectral Signature Plot; spectral signature is calculated from the Input image;
: show the ROI spectral signature in the Spectral Signature Plot; spectral signature is calculated from the Input image;
5.2.6.2. Automatic thresholds¶
Set thresholds automatically for highlighted signatures in the table LC Signature threshold; if no signature is highlighted, then the threshold is applied to all the signatures.
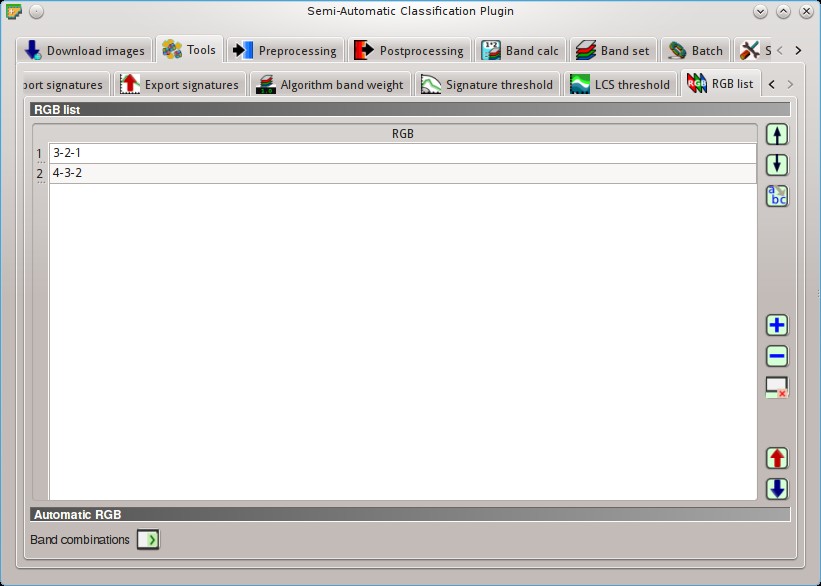
5.2.7. RGB list¶
This tab allows for managing the RGB Color Composite used in the list RGB= of the Image control.
5.2.7.1. RGB list¶
 : move highlighted RGB combination upward;
: move highlighted RGB combination upward; : move highlighted RGB combination downward;
: move highlighted RGB combination downward; : automatically sort RGB combinations by name;
: automatically sort RGB combinations by name; : add a row to the table;
: add a row to the table; : remove highlighted rows from the table;
: remove highlighted rows from the table; : clear all RGB combinations from RGB list;
: clear all RGB combinations from RGB list; : export the RGB list to a file (i.e.
: export the RGB list to a file (i.e. .csv); : import a previously saved RGB list from file (i.e.
: import a previously saved RGB list from file (i.e. .csv);
5.3. Preprocessing¶
The tab  Preprocessing provides several tools for data manipulation which are useful before the actual classification process.
Preprocessing provides several tools for data manipulation which are useful before the actual classification process.
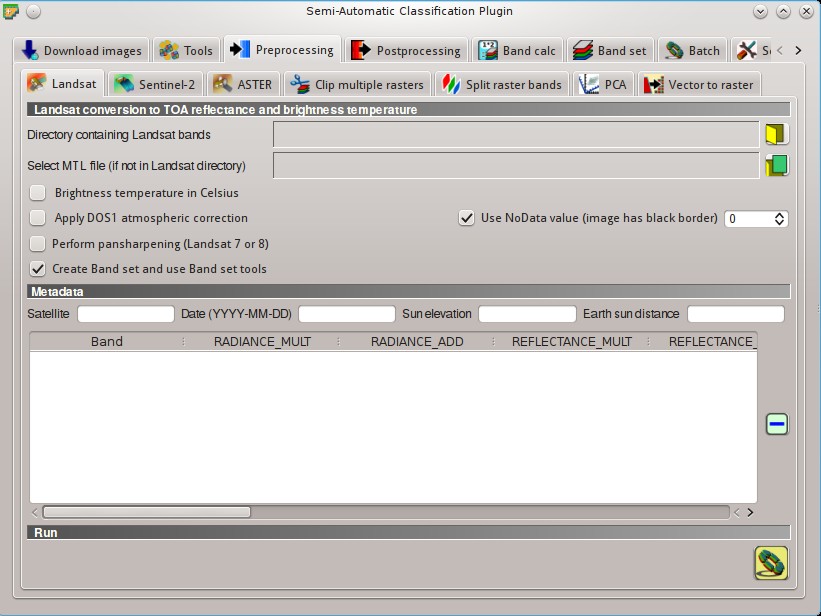
5.3.1. Landsat¶
This tab allows for the conversion of Landsat 1, 2, and 3 MSS and Landsat 4, 5, 7, and 8 images from DN (i.e. Digital Numbers) to the physical measure of Top Of Atmosphere reflectance (TOA), or the application of a simple atmospheric correction using the DOS1 method (Dark Object Subtraction 1), which is an image-based technique (for more information about the Landsat conversion to TOA and DOS1 correction, see Image conversion to reflectance). Pan-sharpening is also available; for more information read Pan-sharpening.
Once the input is selected, available bands are listed in the metadata table.
5.3.1.1. Landsat conversion to TOA reflectance and brightness temperature¶
- Directory containing Landsat bands
 : open a directory containing Landsat bands; names of Landsat bands must end with the corresponding number; if the metadata file is included in this directory then Metadata are automatically filled;
: open a directory containing Landsat bands; names of Landsat bands must end with the corresponding number; if the metadata file is included in this directory then Metadata are automatically filled; - Select MTL file

 : if the metadata file is not included in the Directory containing Landsat bands, select the path of the metadata file in order to fill the Metadata automatically;
: if the metadata file is not included in the Directory containing Landsat bands, select the path of the metadata file in order to fill the Metadata automatically;  Brightness temperature in Celsius: if checked, convert brightness temperature to Celsius (if a Landsat thermal band is listed in Metadata); if unchecked temperature is in Kelvin;
Brightness temperature in Celsius: if checked, convert brightness temperature to Celsius (if a Landsat thermal band is listed in Metadata); if unchecked temperature is in Kelvin; Apply DOS1 atmospheric correction: if checked, the DOS1 Correction is applied to all the bands (thermal bands excluded);
Apply DOS1 atmospheric correction: if checked, the DOS1 Correction is applied to all the bands (thermal bands excluded); Use NoData value (image has black border)
Use NoData value (image has black border)  : if checked, pixels having
: if checked, pixels having NoDatavalue are not counted during conversion and the DOS1 calculation of DNmin; it is useful when image has a black border (usually pixel value = 0); Perform pan-sharpening: if checked, a Brovey Transform is applied for the Pan-sharpening of Landsat bands;
Perform pan-sharpening: if checked, a Brovey Transform is applied for the Pan-sharpening of Landsat bands; Create Band set and use Band set tools: if checked, the Band set is created after the conversion; also, the Band set is processed according to the tools checked in the Band set;
Create Band set and use Band set tools: if checked, the Band set is created after the conversion; also, the Band set is processed according to the tools checked in the Band set;
5.3.1.2. Metadata¶
All the bands found in the Directory containing Landsat bands are listed in the table Metadata. If the Landsat metadata file (a .txt or .met file with the suffix MTL) is provided, then Metadata are automatically filled. For information about Metadata fields read this page and this one .
- Satellite
 : satellite name (e.g. Landsat8);
: satellite name (e.g. Landsat8); - Date
 : date acquired (e.g. 2013-04-15);
: date acquired (e.g. 2013-04-15); - Sun elevation
 : Sun elevation in degrees;
: Sun elevation in degrees; - Earth sun distance
 : Earth Sun distance in astronomical units (automatically calculated if Date is filled;
: Earth Sun distance in astronomical units (automatically calculated if Date is filled;  : remove highlighted bands from the table Metadata;
: remove highlighted bands from the table Metadata; Metadata: table containing the following fields;
Metadata: table containing the following fields;- Band: band name;
- RADIANCE_MULT: multiplicative rescaling factor;
- RADIANCE_ADD: additive rescaling factor;
- REFLECTANCE_MULT: multiplicative rescaling factor;
- REFLECTANCE_ADD: additive rescaling factor;
- RADIANCE_MAXIMUM: radiance maximum;
- REFLECTANCE_MAXIMUM: reflectance maximum;
- K1_CONSTANT: thermal conversion constant;
- K2_CONSTANT: thermal conversion constant;
- LMAX: spectral radiance that is scaled to QCALMAX;
- LMIN: spectral radiance that is scaled to QCALMIN;
- QCALMAX: minimum quantized calibrated pixel value;
- QCALMIN: maximum quantized calibrated pixel value;
5.3.1.3. Run¶
5.3.2. Sentinel-2¶
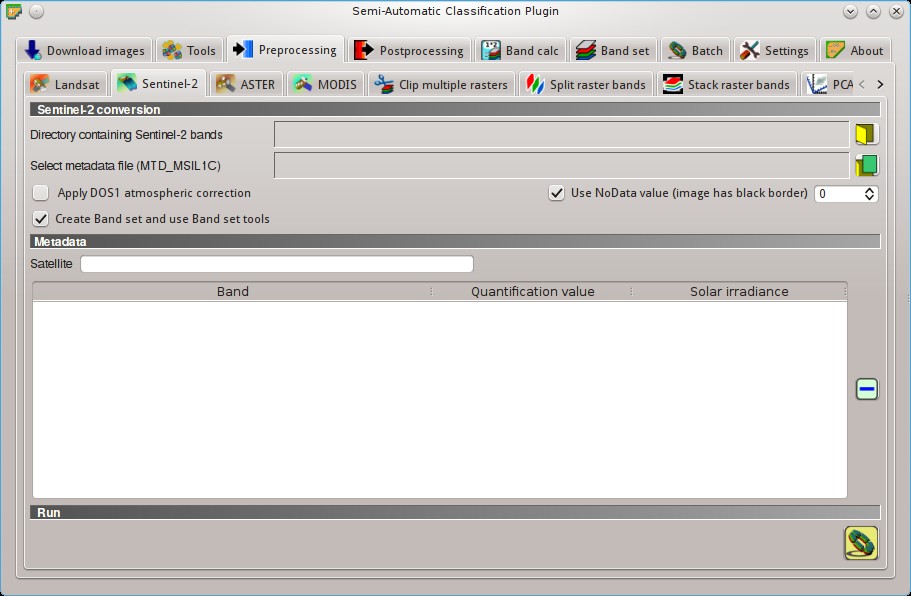
This tab allows for the conversion of Sentinel-2 images to the physical measure of Top Of Atmosphere reflectance (TOA), or the application of a simple atmospheric correction using the DOS1 method (Dark Object Subtraction 1), which is an image-based technique (for more information about conversion to TOA and DOS1 correction, see Image conversion to reflectance).
Once the input is selected, available bands are listed in the metadata table.
5.3.2.1. Sentinel-2 conversion¶
- Directory containing Sentinel-2 bands
 : open a directory containing Sentinel-2 bands; names of Sentinel-2 bands must end with the corresponding number; if the metadata file is included in this directory then Metadata are automatically filled;
: open a directory containing Sentinel-2 bands; names of Sentinel-2 bands must end with the corresponding number; if the metadata file is included in this directory then Metadata are automatically filled; - Select metadata file

 : select the metadata file which is a .xml file whose name contains
: select the metadata file which is a .xml file whose name contains MTD_MSIL1C);  Apply DOS1 atmospheric correction: if checked, the DOS1 Correction is applied to all the bands;
Apply DOS1 atmospheric correction: if checked, the DOS1 Correction is applied to all the bands; Use NoData value (image has black border)
Use NoData value (image has black border)  : if checked, pixels having
: if checked, pixels having NoDatavalue are not counted during conversion and the DOS1 calculation of DNmin; it is useful when image has a black border (usually pixel value = 0); Create Band set and use Band set tools: if checked, the Band set is created after the conversion; also, the Band set is processed according to the tools checked in the Band set;
Create Band set and use Band set tools: if checked, the Band set is created after the conversion; also, the Band set is processed according to the tools checked in the Band set;
5.3.2.2. Metadata¶
All the bands found in the Directory containing Sentinel-2 bands are listed in the table Metadata.
If the Sentinel-2 metadata file (a .xml file whose name contains MTD_MSIL1C) is provided, then Metadata are automatically filled.
For information about Metadata fields read this informative page .
5.3.2.3. Run¶
5.3.3. ASTER¶
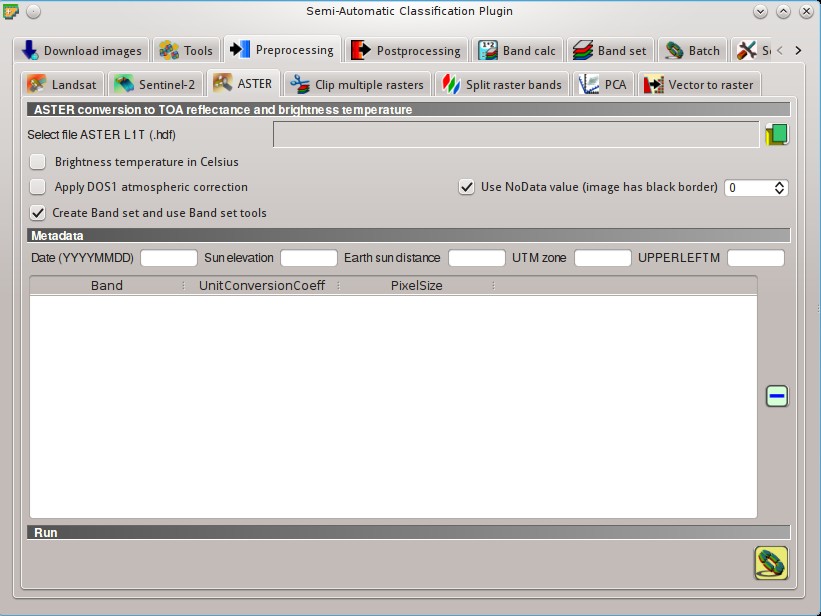
This tab allows for the conversion of ASTER L1T images to the physical measure of Top Of Atmosphere reflectance (TOA), or the application of a simple atmospheric correction using the DOS1 method (Dark Object Subtraction 1), which is an image-based technique (for more information about conversion to TOA and DOS1 correction, see Image conversion to reflectance).
Once the input is selected, available bands are listed in the metadata table.
5.3.3.1. ASTER conversion¶
- Select file ASTER L1T
 : select an ASTER image (file .hdf);
: select an ASTER image (file .hdf);  Apply DOS1 atmospheric correction: if checked, the DOS1 Correction is applied to all the bands;
Apply DOS1 atmospheric correction: if checked, the DOS1 Correction is applied to all the bands; Use NoData value (image has black border)
Use NoData value (image has black border)  : if checked, pixels having
: if checked, pixels having NoDatavalue are not counted during conversion and the DOS1 calculation of DNmin; it is useful when image has a black border (usually pixel value = 0); Create Band set and use Band set tools: if checked, the Band set is created after the conversion; also, the Band set is processed according to the tools checked in the Band set;
Create Band set and use Band set tools: if checked, the Band set is created after the conversion; also, the Band set is processed according to the tools checked in the Band set;
5.3.3.2. Metadata¶
All the bands found in the Select file ASTER L1T are listed in the table Metadata. For information about Metadata fields visit the ASTER page .
- Date
 : date acquired (e.g. 20130415);
: date acquired (e.g. 20130415); - Sun elevation
 : Sun elevation in degrees;
: Sun elevation in degrees; - Earth sun distance
 : Earth Sun distance in astronomical units (automatically calculated if Date is filled;
: Earth Sun distance in astronomical units (automatically calculated if Date is filled; - UTM zone
 : UTM zone code of the image;
: UTM zone code of the image; - UPPERLEFTM
 : coordinates of the upper left corner of the image;
: coordinates of the upper left corner of the image;  : remove highlighted bands from the table Metadata;
: remove highlighted bands from the table Metadata;
5.3.3.3. Run¶
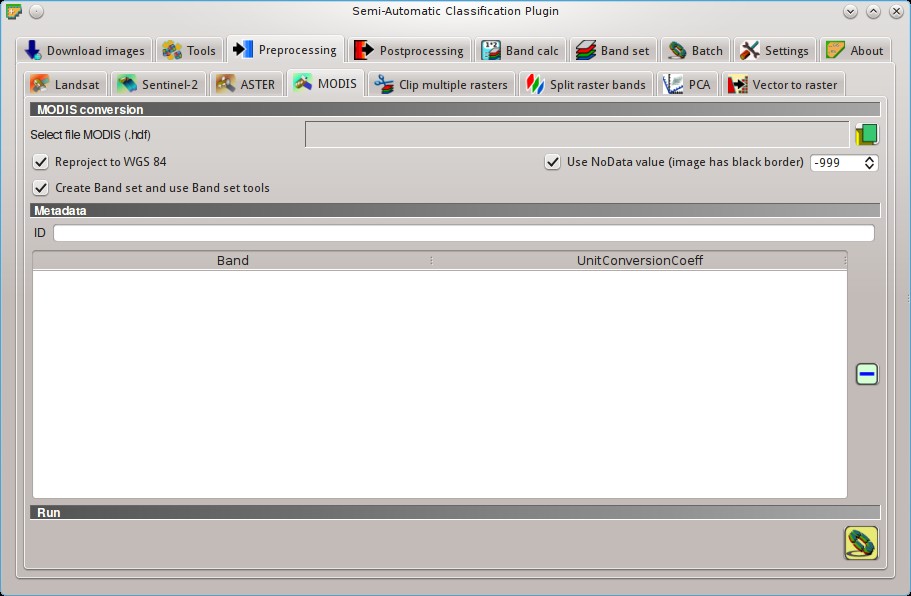
5.3.4. MODIS¶
This tab allows for the conversion of MODIS images to .tif format, and the reprojection to WGS 84.
Once the input is selected, available bands are listed in the metadata table.
5.3.4.1. MODIS conversion¶
- Select file MODIS
 : select a MODIS image (file .hdf);
: select a MODIS image (file .hdf);  Reproject to WGS 84: if checked, reproject bands to WGS 84, required for use in SCP;
Reproject to WGS 84: if checked, reproject bands to WGS 84, required for use in SCP; Use NoData value (image has black border)
Use NoData value (image has black border)  : if checked, pixels having
: if checked, pixels having NoDatavalue are not counted during conversion and the DOS1 calculation of DNmin; it is useful when image has a black border (usually pixel value = 0); Create Band set and use Band set tools: if checked, the Band set is created after the conversion; also, the Band set is processed according to the tools checked in the Band set;
Create Band set and use Band set tools: if checked, the Band set is created after the conversion; also, the Band set is processed according to the tools checked in the Band set;
5.3.4.2. Metadata¶
All the bands found in the Select file MODIS are listed in the table Metadata. For information about Metadata fields visit the MODIS page .
5.3.4.3. Run¶
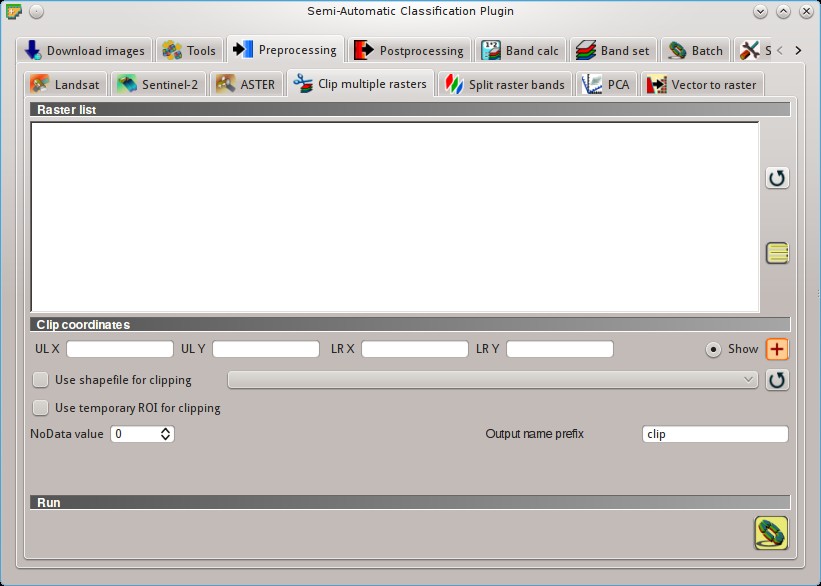
5.3.5. Clip multiple rasters¶
This tab allows for cutting several image bands at once, using a rectangle defined with point coordinates or a boundary defined with a shapefile.
5.3.5.1. Raster list¶
5.3.5.2. Clip coordinates¶
Set the Upper Left (UL) and Lower Right (LR) point coordinates of the rectangle used for clipping; it is possible to enter the coordinates manually. Alternatively use a shapefile.
- UL X
 : set the UL X coordinate;
: set the UL X coordinate; - UL Y
 : set the UL Y coordinate;
: set the UL Y coordinate; - LR X
 : set the LR X coordinate;
: set the LR X coordinate; - LR Y
 : set the LR Y coordinate;
: set the LR Y coordinate;  Show: show or hide the clip area drawn in the map;
Show: show or hide the clip area drawn in the map; : define a clip area by drawing a rectangle in the map; left click to set the UL point and right click to set the LR point; the area is displayed in the map;
: define a clip area by drawing a rectangle in the map; left click to set the UL point and right click to set the LR point; the area is displayed in the map; Use shapefile for clipping
Use shapefile for clipping  : if checked, use the selected shapefile (already loaded in QGIS) for clipping; UL and LR coordinates are ignored;
: if checked, use the selected shapefile (already loaded in QGIS) for clipping; UL and LR coordinates are ignored; Use temporary ROI for clipping: if checked, use a temporary ROI (see ROI creation) for clipping; UL and LR coordinates are ignored;
Use temporary ROI for clipping: if checked, use a temporary ROI (see ROI creation) for clipping; UL and LR coordinates are ignored; : refresh layer list;
: refresh layer list; NoData value
NoData value  : if checked, set the value for
: if checked, set the value for NoDatapixels (e.g. pixels outside the clipped area);- Output name prefix
 : set the prefix for output file names (default is
: set the prefix for output file names (default is clip);
5.3.5.3. Run¶
 : choose an output destination and clip selected rasters; only rasters selected in the Raster list are clipped and automatically loaded in QGIS;
: choose an output destination and clip selected rasters; only rasters selected in the Raster list are clipped and automatically loaded in QGIS;
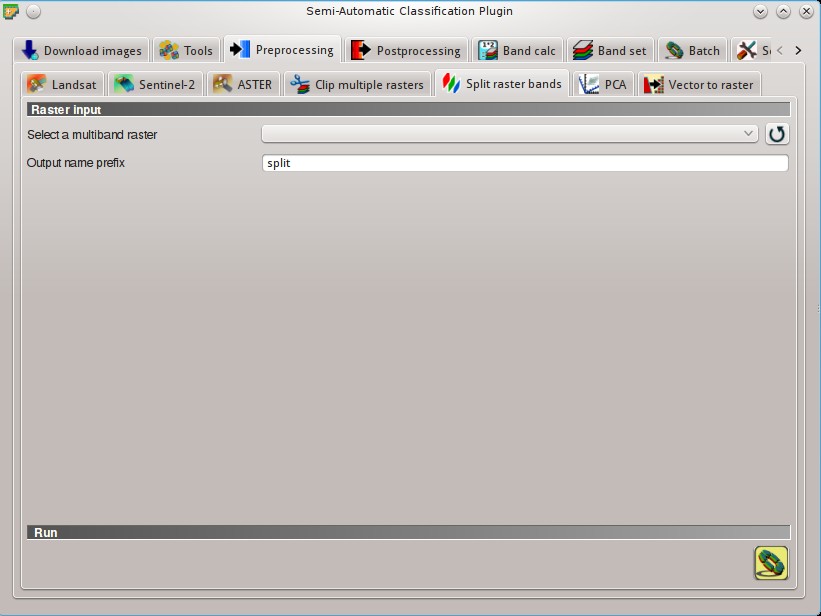
5.3.6. Split raster bands¶
Split a multiband raster to single bands.
5.3.6.1. Raster input¶
5.3.6.2. Run¶
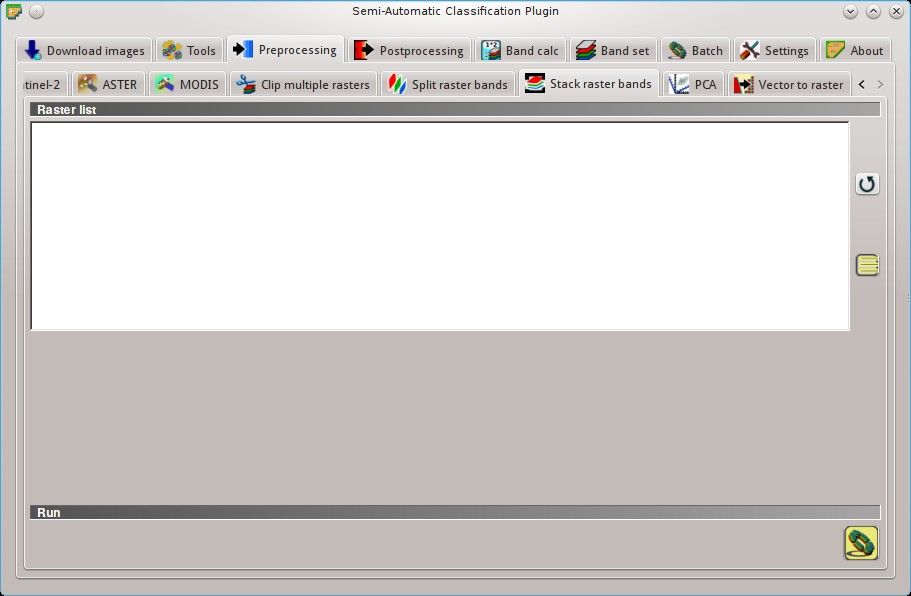
5.3.7. Stack raster bands¶
Stack raster bands into a single file.
5.3.7.1. Raster list¶
5.3.7.2. Run¶
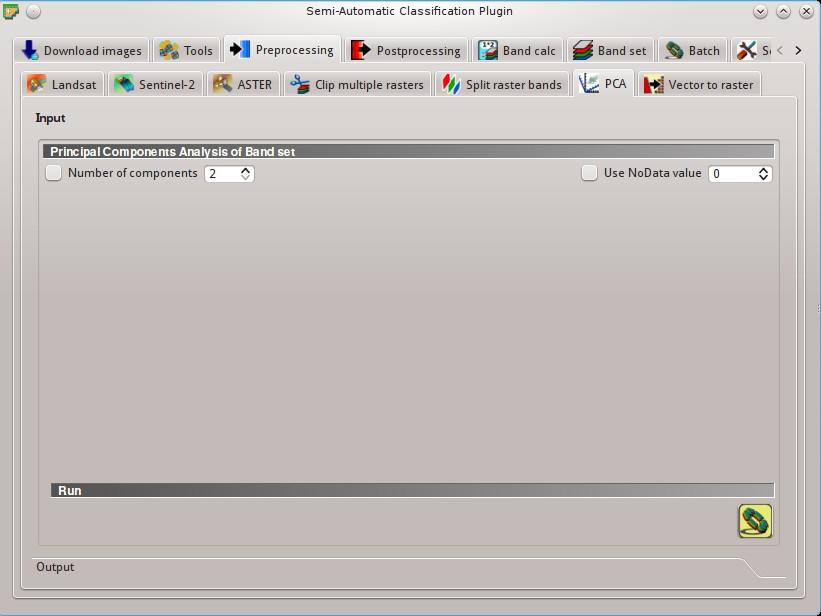
5.3.8. PCA¶
This tab allows for the PCA (Principal Component Analysis) of bands loaded in the Band set.
5.3.8.1. Principal Component Analysis of Band set¶
5.3.8.2. Run¶
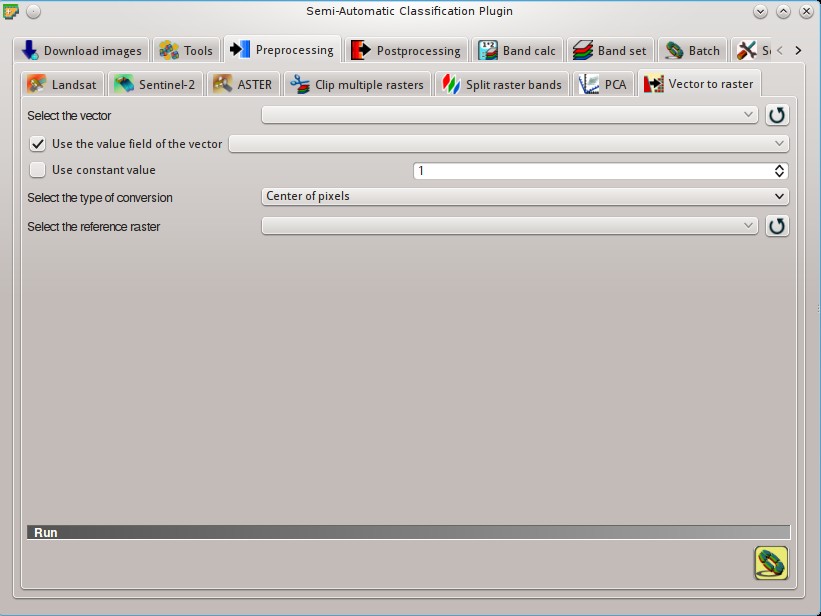
5.3.9. Vector to raster¶
This tab allows for the conversion of a vector to raster format.
- Select the vector
 : select a vector already loaded in QGIS;
: select a vector already loaded in QGIS;  : refresh layer list;
: refresh layer list; Use the value field of the vector
Use the value field of the vector  : if checked, the selected field is used as attribute for the conversion; pixels of the output raster have the same values as the vector attribute;
: if checked, the selected field is used as attribute for the conversion; pixels of the output raster have the same values as the vector attribute; Use constant value
Use constant value  : if checked, the polygons are converted to raster using the selected constant value;
: if checked, the polygons are converted to raster using the selected constant value;- Select the type of conversion
 : select the type of conversion between Center of pixels and All pixels touched:
: select the type of conversion between Center of pixels and All pixels touched: - Center of pixels: during the conversion, vector is compared to the reference raster; output raster pixels are attributed to a polygon if pixel center is within that polygon;
- All pixels touched: during the conversion, vector is compared to the reference raster; output raster pixels are attributed to a polygon if pixel touches that polygon;
- Select the type of conversion
- Select the reference raster
 : select a reference raster; pixels of the output raster have the same size and alignment as the reference raster;
: select a reference raster; pixels of the output raster have the same size and alignment as the reference raster;  : refresh layer list;
: refresh layer list;
5.3.9.1. Run¶
5.4. Postprocessing¶
The tab  Postprocessing provides several functions that can be applied to the classification output.
Postprocessing provides several functions that can be applied to the classification output.
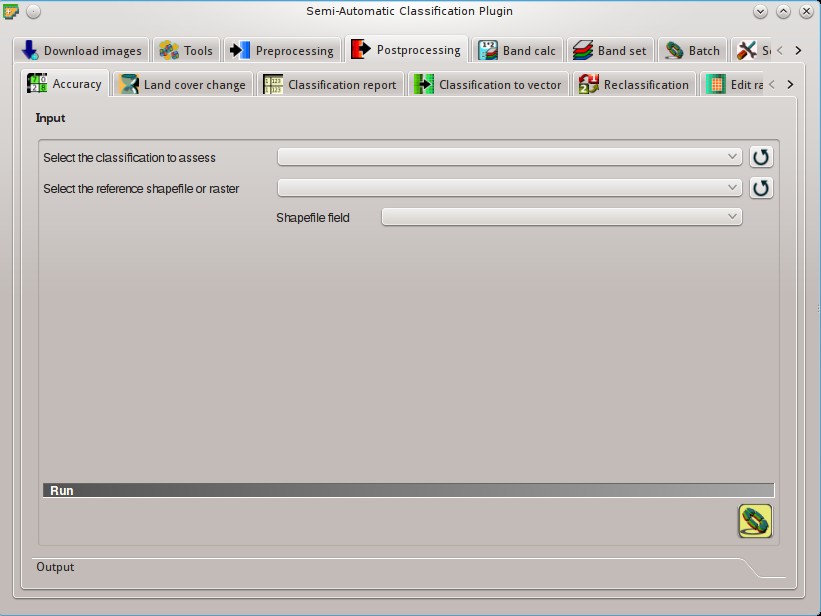
5.4.1. Accuracy¶
This tab allows for the validation of a classification (read Accuracy Assessment ). Classification is compared to a reference raster or reference shapefile (which is automatically converted to raster). If a shapefile is selected as reference, it is possible to choose a field describing class values.
Several statistics are calculated such as overall accuracy, user’s accuracy, producer’s accuracy, and Kappa hat.
The output is an error raster that is a .tif file showing the errors in the map, where pixel values represent the categories of comparison (i.e. combinations identified by the ErrorMatrixCode in the error matrix) between the classification and reference.
Also, a text file containing the error matrix (i.e. a .csv file separated by tab) is created with the same name defined for the .tif file.
5.4.1.1. Input¶
- Select the classification to assess
 : select a classification raster (already loaded in QGIS);
: select a classification raster (already loaded in QGIS);  : refresh layer list;
: refresh layer list;- Select the reference shapefile or raster
 : select a raster or a shapefile (already loaded in QGIS), used as reference layer (ground truth) for the accuracy assessment;
: select a raster or a shapefile (already loaded in QGIS), used as reference layer (ground truth) for the accuracy assessment;  : refresh layer list;
: refresh layer list;- Shapefile field
 : if a shapefile is selected as reference, select a shapefile field containing numeric class values;
: if a shapefile is selected as reference, select a shapefile field containing numeric class values;
5.4.1.2. Run¶
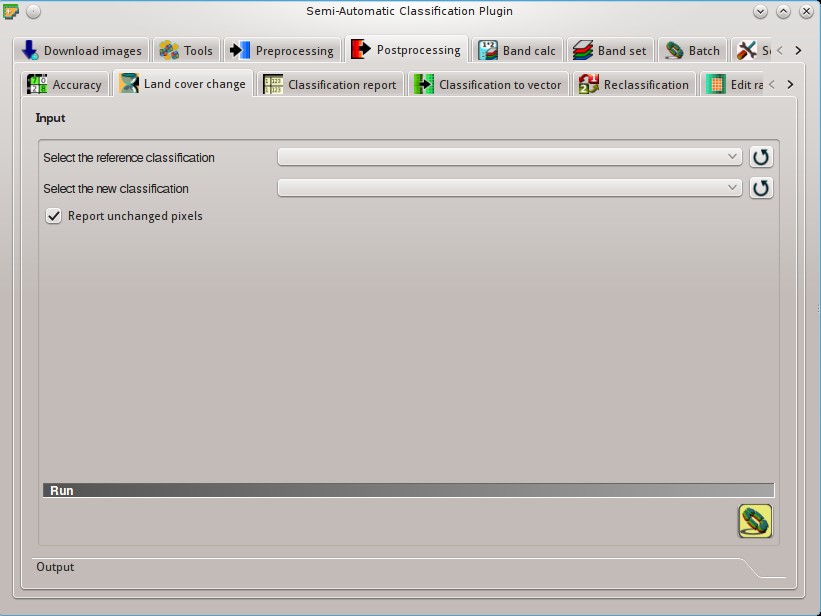
5.4.2. Land cover change¶
The tab Land cover change allows for the comparison between two classifications in order to assess land cover changes.
Output is a land cover change raster (i.e. a file .tif showing the changes in the map, where each pixel represents a category of comparison (i.e. combinations) between the two classifications, which is the ChangeCode in the land cover change statistics) and a text file containing the land cover change statistics (i.e. a file .csv separated by tab, with the same name defined for the .tif file).
5.4.2.1. Input¶
- Select the reference classification
 : select a reference classification raster (already loaded in QGIS);
: select a reference classification raster (already loaded in QGIS);  : refresh layer list;
: refresh layer list;- Select the new classification
 : select a new classification raster (already loaded in QGIS), to be compared with the reference classification;
: select a new classification raster (already loaded in QGIS), to be compared with the reference classification;  : refresh layer list;
: refresh layer list; Report unchanged pixels: if checked, report also unchanged pixels (having the same value in both classifications);
Report unchanged pixels: if checked, report also unchanged pixels (having the same value in both classifications);
5.4.2.2. Run¶
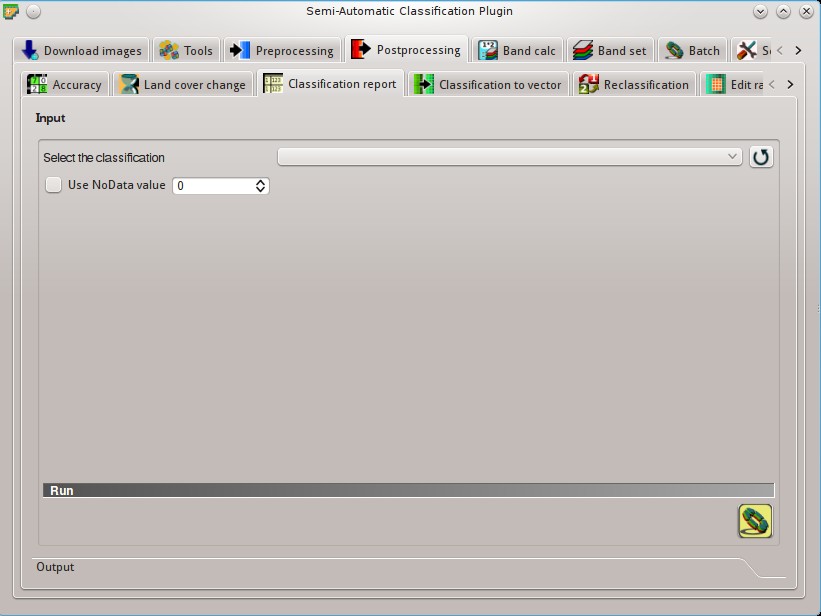
5.4.3. Classification report¶
This tab allows for the calculation of class statistics such as number of pixels, percentage and area (area unit is defined from the image itself).
5.4.3.1. Input¶
5.4.3.2. Run¶
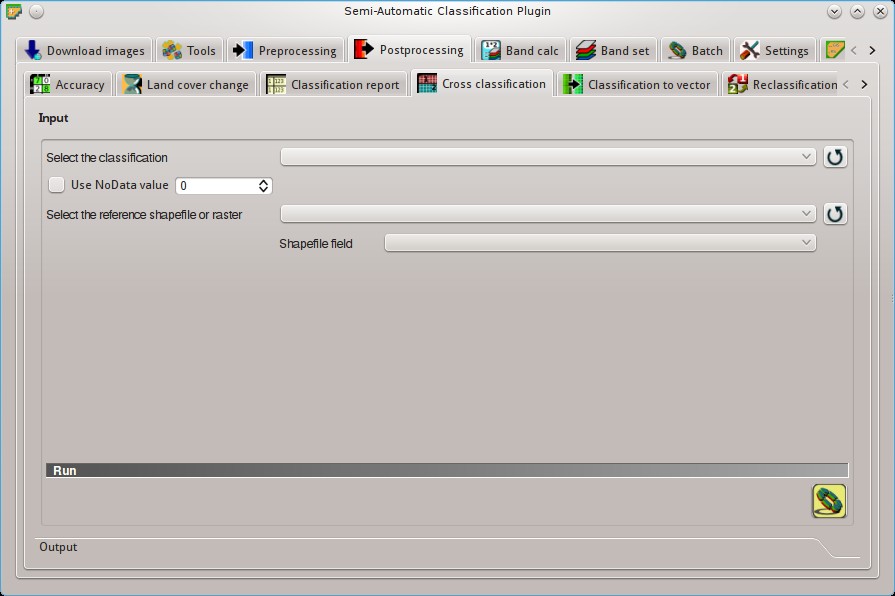
5.4.4. Cross classification¶
This tab allows for the calculation of a cross classification raster and matrix. Classification is compared to a reference raster or reference shapefile (which is automatically converted to raster). This is useful for calculating the area for every combination between reference classes and classification values. If a shapefile is selected as reference, it is possible to choose a field describing class values.
The output is a cross raster that is a .tif file where pixel values represent the categories of comparison (i.e. combinations identified by the CrossMatrixCode) between the classification and reference.
Also, a text file containing the cross matrix (i.e. a .csv file separated by tab) is created with the same name defined for the .tif file.
5.4.4.1. Input¶
- Select the classification
 : select a classification raster (already loaded in QGIS);
: select a classification raster (already loaded in QGIS);  : refresh layer list;
: refresh layer list; Use NoData value
Use NoData value  : if checked,
: if checked, NoDatavalue will be excluded from the calculation;- Select the reference shapefile or raster
 : select a raster or a shapefile (already loaded in QGIS), used as reference layer;
: select a raster or a shapefile (already loaded in QGIS), used as reference layer;  : refresh layer list;
: refresh layer list;- Shapefile field
 : if a shapefile is selected as reference, select a shapefile field containing numeric class values;
: if a shapefile is selected as reference, select a shapefile field containing numeric class values;
5.4.4.2. Run¶
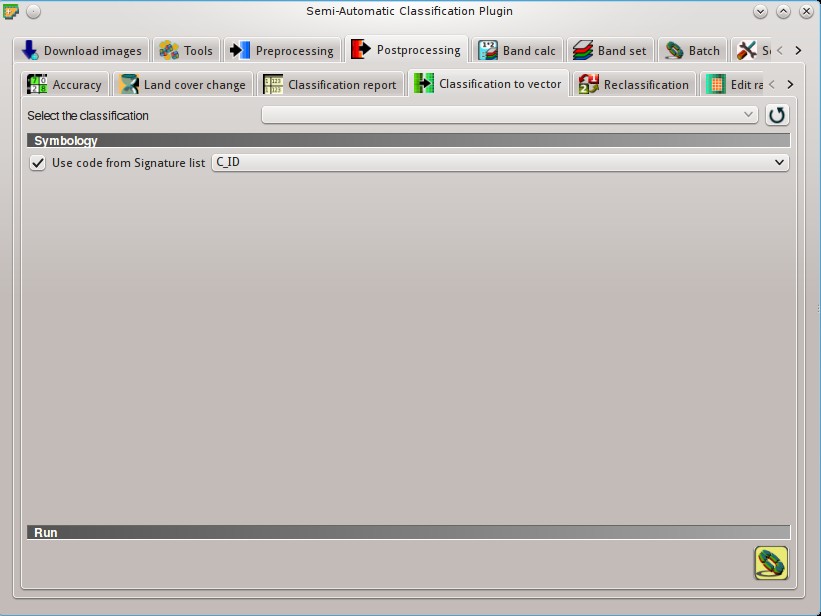
5.4.5. Classification to vector¶
This tab allows for the conversion of a classification raster to vector shapefile.
- Select the classification
 : select a classification raster (already loaded in QGIS);
: select a classification raster (already loaded in QGIS);  : refresh layer list;
: refresh layer list;
5.4.5.1. Symbology¶
 Use code from Signature list
Use code from Signature list  : if checked, color and class information are defined from ROI Signature list:
: if checked, color and class information are defined from ROI Signature list:MC ID: use the ID of macroclasses;C ID: use the ID of classes;
5.4.5.2. Run¶
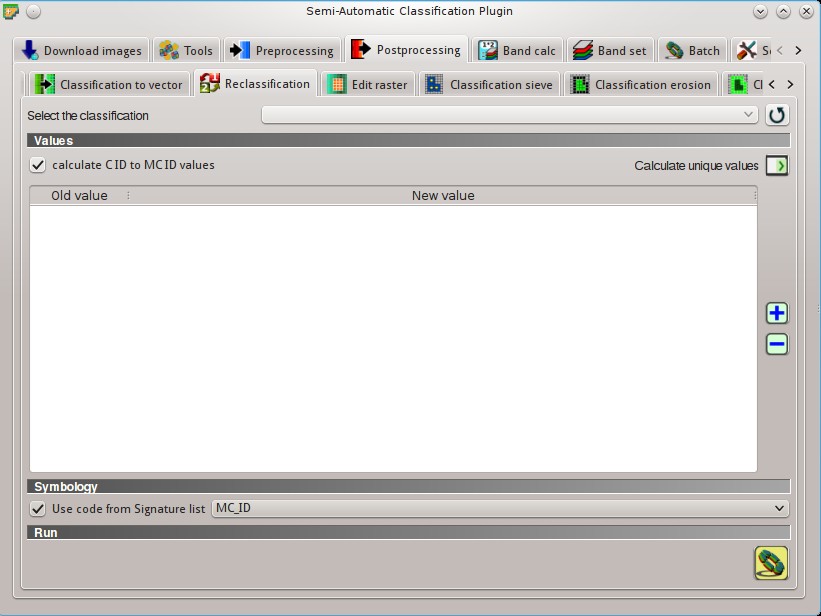
5.4.6. Reclassification¶
This tab allows for the reclassification (i.e. assigning a new class code to raster pixels). In particular, it eases the conversion from C ID to MC ID values.
- Select the classification
 : select a classification raster (already loaded in QGIS);
: select a classification raster (already loaded in QGIS);  : refresh layer list;
: refresh layer list;
5.4.6.1. Values¶
 calculate C ID to MC ID values: if checked, the reclassification table is filled according to the ROI Signature list when Calculate unique values
calculate C ID to MC ID values: if checked, the reclassification table is filled according to the ROI Signature list when Calculate unique values  is clicked;
is clicked;- Calculate unique values
 : calculate unique values in the classification and fill the reclassification table;
: calculate unique values in the classification and fill the reclassification table;  Values: table containing the following fields;
Values: table containing the following fields;- Old value: set the expression defining old values to be reclassified;
Old valuecan be a value or an expressions defined using the variable nameraster(custom names can be defined in Variable name for expressions ), following Python operators (e.g.raster > 3select all pixels having value > 3 ;raster > 5 | raster < 2select all pixels having value > 5 or < 2 ;raster >= 2 & raster <= 5select all pixel values between 2 and 5); - New value: set the new value for the old values defined in
Old value;
- Old value: set the expression defining old values to be reclassified;
 : add a row to the table;
: add a row to the table; : remove highlighted rows from the table;
: remove highlighted rows from the table;
5.4.6.2. Symbology¶
 Use code from Signature list
Use code from Signature list  : if checked, color and class information are defined from ROI Signature list:
: if checked, color and class information are defined from ROI Signature list:MC ID: use the ID of macroclasses;C ID: use the ID of classes;
5.4.6.3. Run¶
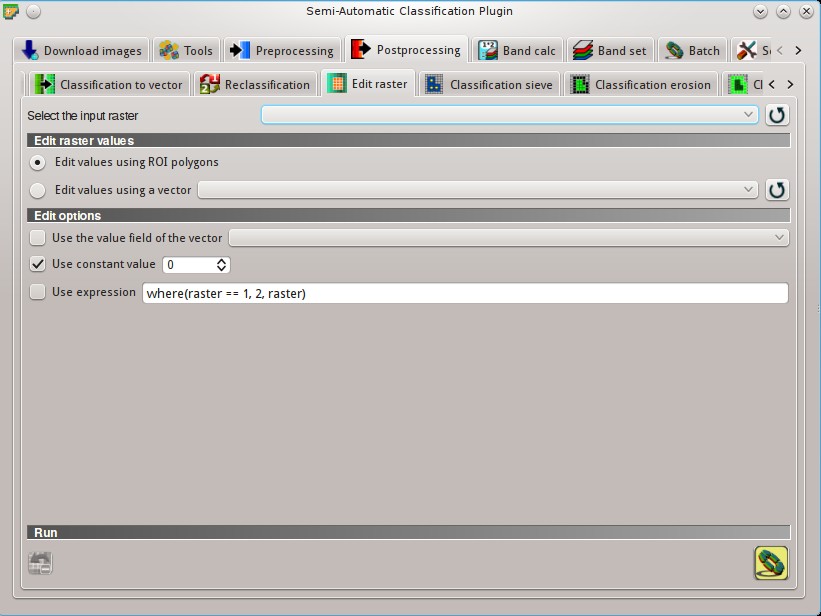
5.4.7. Edit raster¶
This tab allows for the direct editing of pixel values in a raster. Only pixels beneath ROI polygons or vector polygons are edited.
Attention: the input raster is directly edited; it is recommended to create a backup copy of the input raster before using this tool in order to prevent data loss.
This tool can rapidly edit large rasters, especially when editing polygons are small, because pixel values are edited directly. In addition, the SCP Edit Toolbar is available for easing the raster editing using multiple values.
5.4.7.1. Edit raster values¶
5.4.7.2. Edit options¶
 Use the value field of the vector
Use the value field of the vector  : if checked, raster is edited using the selected vector (in Edit values using a vector) and the polygon values of selected vector field;
: if checked, raster is edited using the selected vector (in Edit values using a vector) and the polygon values of selected vector field; Use constant value
Use constant value  : if checked, raster is edited using the selected constant value;
: if checked, raster is edited using the selected constant value; Use expression
Use expression  : if checked, raster is edited according to the entered expression; the expression must contain one or more
: if checked, raster is edited according to the entered expression; the expression must contain one or more where; the following example expressionwhere(raster == 1, 2, raster)is already entered, which sets 2 whererasterequals 1, and leaves unchanged the values whererasteris not equal to 1;
5.4.7.3. Run¶
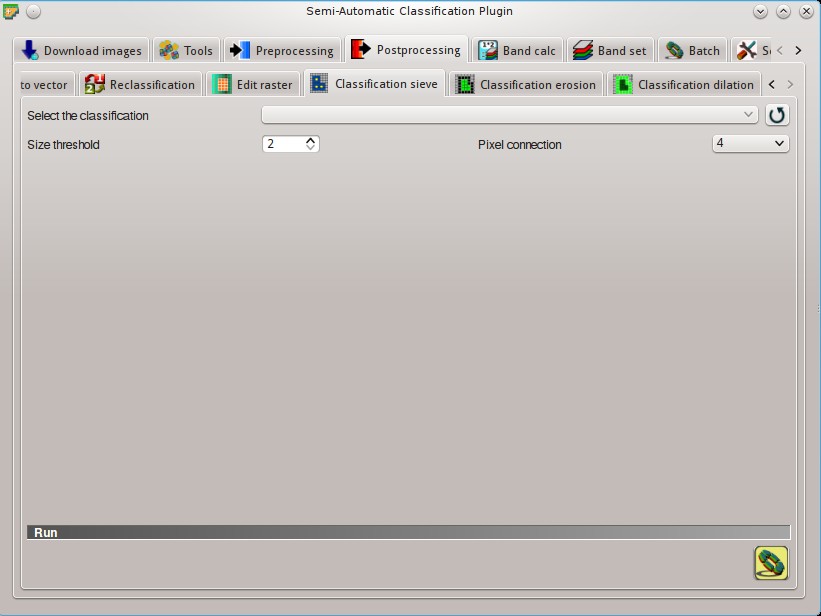
5.4.8. Classification sieve¶
This tab allows for the replacement of isolated pixel values with the value of the largest neighbour patch (based on GDAL Sieve ). It is useful for removing small patches from a classification.
- Select the classification
 : select a raster (already loaded in QGIS);
: select a raster (already loaded in QGIS);  : refresh layer list;
: refresh layer list;- Size threshold
 : size of the patch to be replaced (in pixel unit); all patches smaller the the selected number of pixels will be replaced by the value of the largest neighbour patch;
: size of the patch to be replaced (in pixel unit); all patches smaller the the selected number of pixels will be replaced by the value of the largest neighbour patch;
5.4.8.1. Run¶
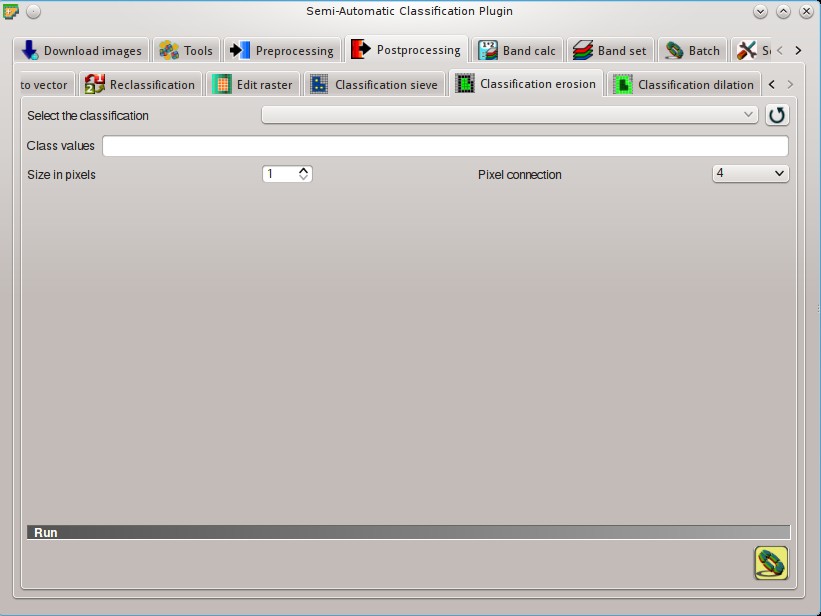
5.4.9. Classification erosion¶
This tab allows for removing the border of a class patch (erosion), defining the class values to be eroded and the number of pixels from the border. It is useful for classification refinement.
- Select the classification
 : select a raster (already loaded in QGIS);
: select a raster (already loaded in QGIS);  : refresh layer list;
: refresh layer list;- Class values
 : set the class values to be eroded; class values must be separated by
: set the class values to be eroded; class values must be separated by ,and-can be used to define a range of values (e.g.1, 3-5, 8will select classes 1, 3, 4, 5, 8); if the text is red then the expression contains errors; - Size in pixels
 : number of pixels to be eroded from the border;
: number of pixels to be eroded from the border;
5.4.9.1. Run¶
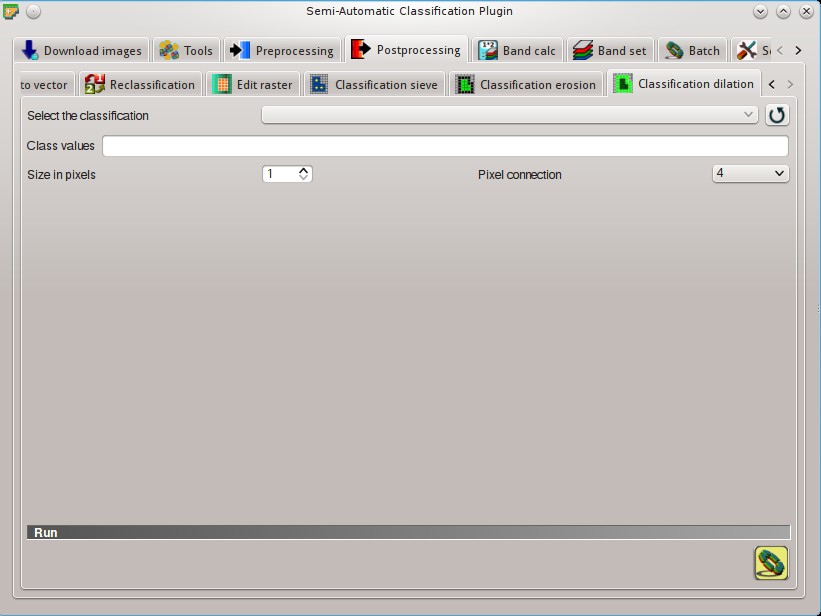
5.4.10. Classification dilation¶
This tab allows for dilating the border of a class patch, defining the class values to be dilated and the number of pixels from the border. It is useful for classification refinement.
- Select the classification
 : select a raster (already loaded in QGIS);
: select a raster (already loaded in QGIS);  : refresh layer list;
: refresh layer list;- Class values
 : set the class values to be dilated; class values must be separated by
: set the class values to be dilated; class values must be separated by ,and-can be used to define a range of values (e.g.1, 3-5, 8will select classes 1, 3, 4, 5, 8); if the text is red then the expression contains errors; - Size in pixels
 : number of pixels to be dilated from the border;
: number of pixels to be dilated from the border;
5.4.10.1. Run¶
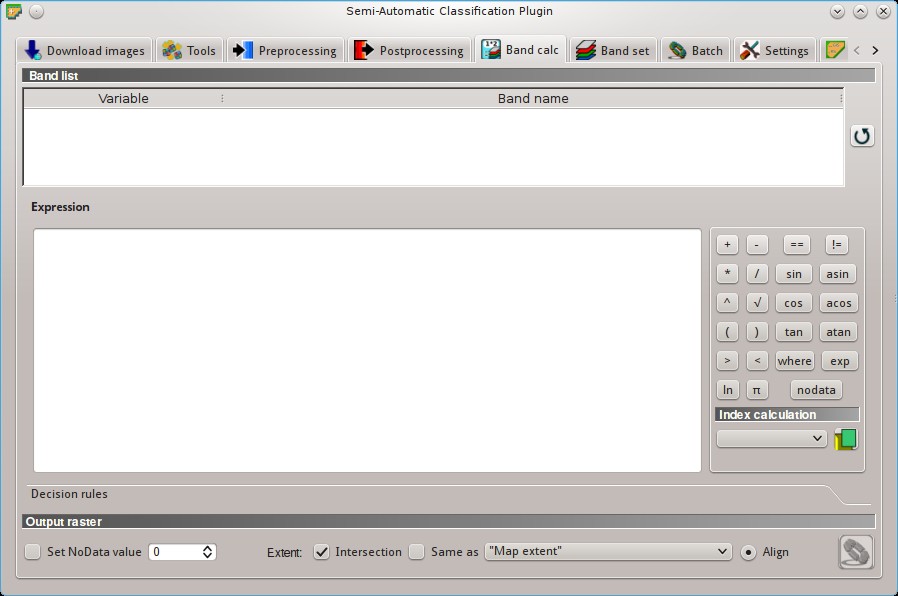
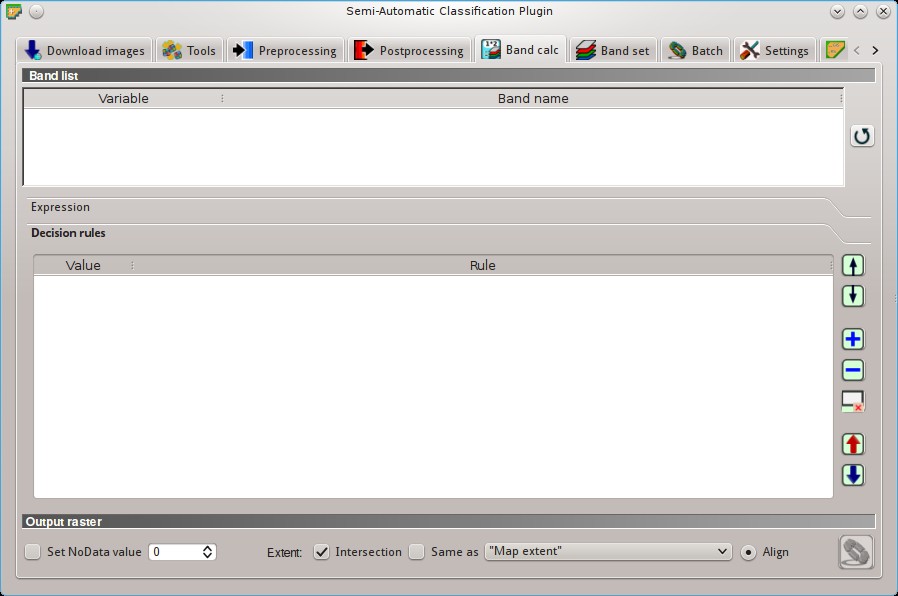
5.5. Band calc¶
The Band calc allows for the raster calculation for bands (i.e. calculation of pixel values) using NumPy functions .
Raster bands must be already loaded in QGIS.
Input rasters must be in the same projection.
In addition, it is possible to calculate a raster using decision rules.
5.5.2. Expression¶
Enter a mathematical expression for raster bands.
In particular, NumPy functions can be used with the prefix np. (e.g. np.log10(raster1) ).
For a list of NumPy functions see the NumPy page .
The expression can work with both Variable and Band name (between double quotes).
Also, bands in the Band set can be referenced directly; for example bandset#b1 refers to band 1 of the Band set.
Double click on any item in the Band list for adding its name to the expression.
In addition, the following variables related to Band set the are available:
- “#BLUE#”: the band with the center wavelength closest to 0.475 \(\mu m\);
- “#RED#”: the band with the center wavelength closest to 0.65 \(\mu m\);
- “#NIR#”: the band with the center wavelength closest to 0.85 \(\mu m\);
Variables for output name are available:
- #BANDSET#: the name of the first band in the Band set;
- #DATE#: the current date and time (e.g. 20161110_113846527764);
If text in the Expression is green, then the syntax is correct; if text is red, then the syntax is incorrect and it is not possible to execute the calculation.
It is possible to enter multiple expressions separated by newlines such as the following example:
"raster1" + "raster2"
"raster3" - "raster4"
The above example calculates two new rasters in the output directory with the suffix _1 (e.g. calc_raster_1 ) for the first expression and _2 (e.g. calc_raster_2 ) for the second expression.
Also, it is possible to define the output name using the symbol @ followed by the name, such as the following example:
"raster1" + "raster2" @ calc_1
"raster3" - "raster4" @ calc_2
The following buttons are available:
- +: plus;
- -: minus;
- *: product;
- /: ratio;
- ^: power;
- V: square-root;
- (: open parenthesis;
- ): close parenthesis;
- >: greater then;
- <: less then;
- ln: natural logarithm;
- π: pi;
- ==: equal;
- !=: not equal;
- sin: sine;
- asin: inverse sine;
- cos: cosine;
- acos: inverse cosine;
- tan: tangent;
- atan: inverse tangent;
- where: conditional expression according to the syntax
where( condition , value if true, value if false)(e.g.where("raster1" == 1, 2, "raster1")); - exp: natural exponential;
- nodata: NoData value of raster (e.g.
nodata("raster1")); it can be used as value in the expression (e.g.where("raster1" == nodata("raster1"), 0, "raster1"));
5.5.3. Index calculation¶
Index calculation allows for entering a spectral index expression (see Spectral Indices).
- Index calculation
 : list of spectral indices:
: list of spectral indices: - NDVI: if selected, the NDVI calculation is entered in the Expression (
(( "#NIR#" - "#RED#") / ( "#NIR#" + "#RED#") @ NDVI)); - EVI: if selected, the EVI calculation is entered in the Expression (
2.5 * ( "#NIR#" - "#RED#" ) / ( "#NIR#" + 6 * "#RED#" - 7.5 * "#BLUE#" + 1) @ EVI);
- NDVI: if selected, the NDVI calculation is entered in the Expression (
- Index calculation
 : open a text file (.txt) containing custom expressions to be listed in Index calculation; the text file must contain an expression for each line; each line must be in the form
: open a text file (.txt) containing custom expressions to be listed in Index calculation; the text file must contain an expression for each line; each line must be in the form expression_name; expression(separated by;) where theexpression_nameis the expression name that is displayed in the Index calculation; if you open an empty text file, the default values are restored; following an example of text content:NDVI; ( "#NIR#" - "#RED#" ) / ( "#NIR#" + "#RED#" ) @NDVI EVI; 2.5 * ( "#NIR#" - "#RED#" ) / ( "#NIR#" + 6 * "#RED#" - 7.5 * "#BLUE#" + 1) @EVI SR; ( "#NIR#" / "#RED#" ) @SR
5.5.4. Decision rules¶
Decision rules allows for the calculation of an output raster based on rules. Rules are conditional statements based on other rasters; if the Rule is true, the corresponding Value is assigned to the output pixel.
Rules are verified from the first to the last row in the table; if the first Rule is false, the next Rule is verified for that pixel, until the last rule.
If multiple rules are true for a certain pixel, the value of the first Rule is assigned to that pixel.
The NoData value is assigned to those pixels where no Rule is true.
 Decision rules: table containing the following fields;
Decision rules: table containing the following fields;- Value: the value assigned to pixels if the Rule is true;
- Rule: the rule to be verified (e.g.
"raster1" > 0); multiple conditional statements can be entered separated by;(e.g."raster1" > 0; "raster2" < 1which means to set the Value whereraster1> 0 andraster2< 1);
 : move highlighted rule up;
: move highlighted rule up; : move highlighted rule down;
: move highlighted rule down; : add a new row to the table;
: add a new row to the table; : delete the highlighted rows from the table;
: delete the highlighted rows from the table; : clear the table;
: clear the table; : export the rules to a text file that can be imported later;
: export the rules to a text file that can be imported later; : import rules from a text file;
: import rules from a text file;
5.5.5. Output raster¶
The output raster is a .tif file, with the same spatial resolution and projection of input rasters; if input rasters have different spatial resolutions, then the highest resolution (i.e. minimum pixel size) is used for output raster.
 Use NoData value
Use NoData value  : if checked, set the value of
: if checked, set the value of NoDatapixels in output raster;- Extent: if the following options are unchecked, the output raster extent will include the extents of all input rasters;
 Align: if checked, and
Align: if checked, and  Same as is checked selecting a raster, the calculation is performed using the same extent and pixel alignment of selected raster;
Same as is checked selecting a raster, the calculation is performed using the same extent and pixel alignment of selected raster; : if
: if Expressionis active and text is green, choose the output destination and start the calculation based onExpression; ifDecision rulesis active and text is green, choose the output destination and start the calculation based onDecision rules;
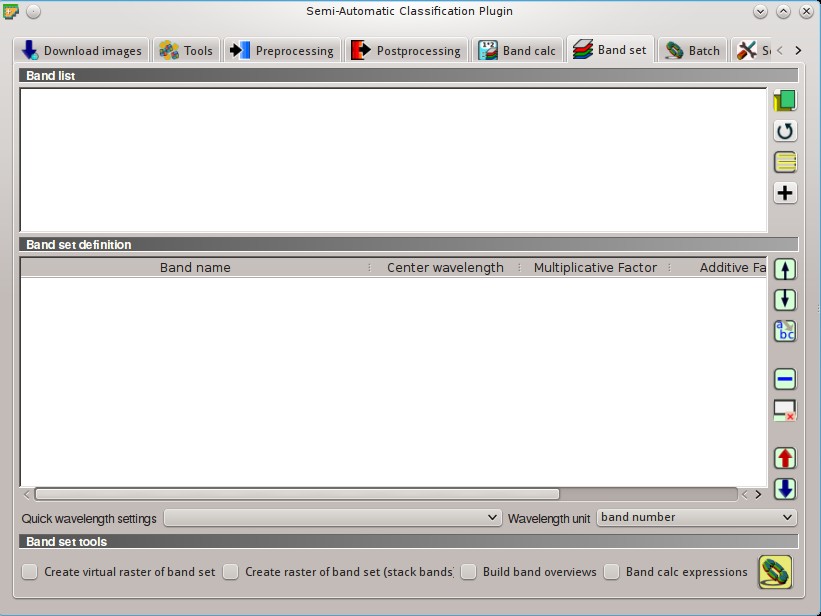
5.6. Band set¶
This tab allows for the definition of a set of single band rasters (Band set) used as Input image.
The Center wavelength of bands should be defined in order to use several functions of SCP.
If a Band set of single band rasters is defined, then the item << band set >> will be listed in the Working toolbar as input image.
The Band set definition is saved with the QGIS project.
5.6.1. Band list¶
List of single band rasters loaded in QGIS.
5.6.2. Band set definition¶
Definition of bands composing the input image .
If the Center wavelength of bands is not defined, the band number is used and some SCP tools will be disabled.
It is possible to define a multiplicative rescaling factor and additive rescaling factor for each band (for instance using the values in Landsat metadata), which are used on the fly (i.e. pixel value = original pixel value * multiplicative rescaling factor + additive rescaling factor) during the processing.
 : move highlighted bands upward;
: move highlighted bands upward; : move highlighted bands downward;
: move highlighted bands downward; : sort automatically bands by name, giving priority to the ending numbers of name;
: sort automatically bands by name, giving priority to the ending numbers of name; : remove highlighted bands from the Band set;
: remove highlighted bands from the Band set; : clear all bands from Band set;
: clear all bands from Band set; : export the Band set to a file;
: export the Band set to a file; : import a previously saved Band set from file;
: import a previously saved Band set from file;- Quick wavelength settings

 : rapid definition of band center wavelength for the following satellite sensors:
: rapid definition of band center wavelength for the following satellite sensors: - ASTER;
- GeoEye-1;
- Landsat 8 OLI;
- Landsat 7 ETM+;
- Landsat 5 TM;
- Landsat 4 TM;
- Landsat 1, 2, and 3 MSS;
- MODIS;
- Pleiades;
- QuickBird;
- RapidEye;
- Sentinel-2;
- SPOT 4;
- SPOT 5;
- SPOT 6;
- WorldView-2 and WorldView-3;
- Quick wavelength settings
5.6.3. Band set tools¶
It is possible to perform several processes directly on Band set.
 Create virtual raster of band set: if checked, create a virtual raster of bands;
Create virtual raster of band set: if checked, create a virtual raster of bands; Create raster of band set (stack bands): if checked, stack all the bands and create a unique .tif raster;
Create raster of band set (stack bands): if checked, stack all the bands and create a unique .tif raster; Build band overviews: if checked, build raster overviews (i.e. pyramids) for improving display performance; overview files are created in the same directory as bands;
Build band overviews: if checked, build raster overviews (i.e. pyramids) for improving display performance; overview files are created in the same directory as bands; Band calc expression: if checked, calculate the Expression entered in Band calc; it is recommended the use of Band set variables in the expression (e.g.
Band calc expression: if checked, calculate the Expression entered in Band calc; it is recommended the use of Band set variables in the expression (e.g. bandset#b1); : choose the output destination and start the process;
: choose the output destination and start the process;
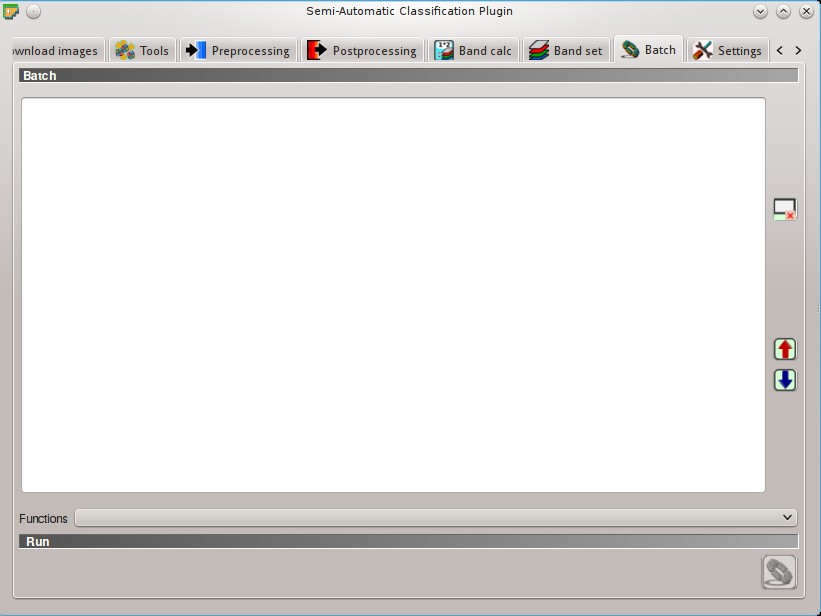
5.7. Batch¶
This tab allows for the automatic execution (batch) of several SCP functions using a scripting interface.
5.7.1. Batch¶
Enter a batch expression; each function must be in a new line. Functions have the following structure:
function name;function options
Each functions has options, identified by a name, with the following structure:
option name:option argument
Options must be separated by the character ; .
Each function option represents an option in the corresponding interface of SCP; option arguments of type text must be between the character ' ; in case of checkboxes, the value 1 represents checked, while the value 0 represents unchecked.
A new line beginning with # can be used for commenting.
According to the function, some of the options are mandatory while other options can be omitted from the expression. Option names that contain path require the full path to a file.
Some options that require multiple arguments such as lists; lists must be separated by , .
If the expression contains errors, the text is red.
 : clear the expression;
: clear the expression; : export the batch expression to a file;
: export the batch expression to a file; : import a previously saved batch expression from file;
: import a previously saved batch expression from file;
- Functions: the following functions are available with the corresponding options;
- Accuracy: calculate accuracy (
accuracy;classification_file_path : '';reference_file_path : '';shapefile_field_name : '';output_raster_path : ''); - ASTER: ASTER conversion (
aster_conversion;input_raster_path : '';celsius_temperature : 0;apply_dos1 : 0;use_nodata : 1;nodata_value : 0;create_bandset : 1;output_dir : ''); - Band calc: band calculation (
band_calc;expression : '';output_raster_path : '';extent_same_as_raster_name : '';extent_intersection : 1;set_nodata : 0;nodata_value : 0); - Classification output: perform classification (
classification;use_macroclass : 0;algorithm_name : 'Minimum Distance';use_lcs : 0;use_lcs_algorithm : 0;use_lcs_only_overlap : 0;apply_mask : 0;mask_file_path : '';vector_output : 0;classification_report : 0;save_algorithm_files : 0;output_classification_path : ''); - Classification dilation: dilation of a classification (
classification_dilation;input_raster_path : '';class_values : '';size_in_pixels : 1;pixel_connection : 4;output_raster_path : ''); - Classification erosion: erosion of a classification (
classification_erosion;input_raster_path : '';class_values : '';size_in_pixels : 1;pixel_connection : 4;output_raster_path : ''); - Classification report: report of a classification (
classification_report;input_raster_path : '';use_nodata : 0;nodata_value : 0;output_report_path : ''); - Classification sieve: classification sieve(
classification_sieve;input_raster_path : '';size_threshold : 2;pixel_connection : 4;output_raster_path : ''); - Classification to vector: convert classification to vector (
classification_to_vector;input_raster_path : '';use_signature_list_code : 1;code_field : 'C_ID';output_vector_path : ''); - Clip multiple rasters: clip multiple rasters (
clip_multiple_rasters;input_raster_path : '';output_dir : '';use_shapefile : 0;shapefile_path : '';ul_x : '';ul_y : '';lr_x : '';lr_y : '';nodata_value : 0;output_name_prefix : 'clip'); - Cross classification: cross classification (
cross_classification;classification_file_path : '';use_nodata : 0;nodata_value : 0;reference_file_path : '';shapefile_field_name : '';output_raster_path : ''); - Edit raster: edit raster values using a shapefile); (
edit_raster_using_shapefile;input_raster_path : '';input_vector_path : '';vector_field_name : '';constant_value : 0;expression : 'where(raster == 1, 2, raster)'); - Land cover change: calculate land cover change (
land_cover_change;reference_raster_path : '';new_raster_path : '';output_raster_path : ''); - Landsat: Landsat conversion (
landsat_conversion;input_dir : '';mtl_file_path : '';celsius_temperature : 0;apply_dos1 : 0;use_nodata : 1;nodata_value : 0;pansharpening : 0;create_bandset : 1;output_dir : ''); - MODIS: MODIS conversion (
modis_conversion;input_raster_path : '';reproject_wgs84 : 1;use_nodata : 1;nodata_value : -999;create_bandset : 1;output_dir : ''); - PCA: Principal Component Analysis (
pca;use_number_of_components : 0, number_of_components : 2;use_nodata : 1;nodata_value : 0;output_dir : ''); - Reclassification: raster reclassification (
reclassification;input_raster_path : '';value_list : 'oldVal-newVal;oldVal-newVal';use_signature_list_code : 1;code_field : 'MC_ID';output_raster_path : ''); - Sentinel-2: Sentinel-2 conversion (
sentinel_conversion;input_dir : '';mtd_safl1c_file_path : '';apply_dos1 : 0;use_nodata : 1;nodata_value : 0;create_bandset : 1;output_dir : ''); - Split raster bands: split raster to single bands (
split_raster_bands;input_raster_path : '';output_dir : '';output_name_prefix : 'split'); - Stack raster bands: stack rasters into a single file (
stack_raster_bands;input_raster_path : '';output_raster_path : ''); - Vector to raster: convert vector to raster (
vector_to_raster;vector_file_path : '';use_value_field : 1;vector_field_name : '';constant_value : 1;reference_raster_path : '';type_of_conversion : 'Center of pixels';output_raster_path : '');
- Accuracy: calculate accuracy (
- In addition, the following functions are available:
- Add raster to QGIS: add a raster to QGIS (
add_raster;input_raster_path : '';input_raster_name : ''); - Create Band set: create a Band set (
create_bandset;raster_path_list : '';center_wavelength : '';wavelength_unit : 1;multiplicative_factor : '';additive_factor : ''); - Open training input: open a training input file (
open_training_input;training_file_path : ''); - Set working directory: set a working directory (argument is the path to a directory) (
!working_dir!;'');
- Add raster to QGIS: add a raster to QGIS (
If a working directory is defined, !working_dir! can be entered in other functions where a path is required (e.g. add_raster;input_raster_path : '!working_dir!/raster1.tif';input_raster_name : 'raster1.tif');
An example of batch expression is:
!working_dir!; '/home/user/Desktop/temp/'
add_raster;input_raster_path : '!working_dir!/raster1.tif';input_raster_name : 'raster1.tif'
band_calc;expression : 'where("raster1.tif" > 1, 1,0)';output_raster_path : '!working_dir!/calc1.tif';set_nodata : 1;nodata_value : 0
band_calc;expression : '"raster1.tif" * "calc1.tif"';output_raster_path : '!working_dir!/calc2.tif';extent_intersection : 0
5.8. Settings¶
The tab  Settings allows for the customization of SCP.
Settings allows for the customization of SCP.
5.8.1. Interface¶
Customization of the interface.
5.8.1.1. Field names of training input¶
Set the names of fields in the Training input . Changing field names should usually be avoided.
- MC ID field

 : name of the Macroclass ID field (default is
: name of the Macroclass ID field (default is MC_ID); - MC Info field

 : name of the Macroclass Information field (default is
: name of the Macroclass Information field (default is MC_info); - C ID field

 : name of the Class ID field (default is
: name of the Class ID field (default is C_ID); - C Info field

 : name of the Class Information field (default is
: name of the Class Information field (default is C_info);  : reset field names to default;
: reset field names to default;
5.8.1.2. ROI style¶
Change ROI color and transparency for a better visualization of temporary ROIs on the map.
5.8.1.3. Variable name for expressions¶
Set the variable name used in expressions of the Reclassification and Edit raster .
5.8.1.4. Temporary group name¶
Set the temporary group name in QGIS Layers used for temporary layers .
5.8.1.5. Dock¶
5.8.2. Processing¶
5.8.2.1. Classification process¶
 Play sound when finished
Play sound when finished  : if checked, play a sound when the classification process is completed;
: if checked, play a sound when the classification process is completed; Use virtual rasters for temp files
Use virtual rasters for temp files  : if checked, create virtual rasters for certain temporary files, instead of creating real rasters; it is useful for reducing disk space usage during calculations;
: if checked, create virtual rasters for certain temporary files, instead of creating real rasters; it is useful for reducing disk space usage during calculations; Raster compression
Raster compression  : if checked, a lossless compression (DEFLATE or PACKBITS) is applied to raster outputs in order to save disk space; it is recommended to check this option, however compressed files are sometimes larger than files without compression;
: if checked, a lossless compression (DEFLATE or PACKBITS) is applied to raster outputs in order to save disk space; it is recommended to check this option, however compressed files are sometimes larger than files without compression;
5.8.2.2. RAM¶
5.8.2.3. Temporary directory¶
5.8.3. Debug¶
Debugging utilities for the creation of a Log file (i.e. recording of SCP activities for reporting issues) and testing SCP dependencies.
If you found a plugin error, please read How can I report an error? .